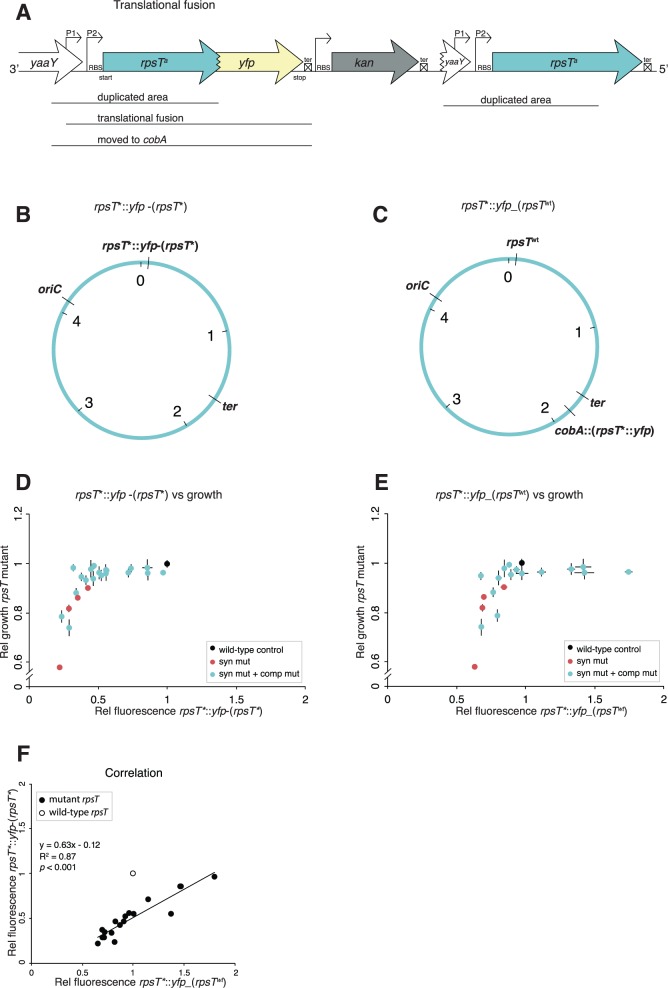
Fig. 5.
rpsT expression measured by fusions of the rpsT gene to the reporter gene yfp. (A) Translational fusions of rpsT to yfp. aindicates different alleles of the rpsT gene. (B) Chromosomal location of the fusion described in (A). The construct was created through insertion duplication as described in supplementary fig. S6, Supplementary Material online, resulting in the rpsT::yfp fusion located next to the original rpsT gene with the same mutations as present in the fusion. We named this fusion rpsT*::yfp-(rpsT*). (C) Chromosomal location of fusions moved to a neutral position close to the terminus (cobA). A wild-type copy of rpsT is present in its native position. We named this fusion rpsT*::yfp_(rpsTwt). (D) Fluorescence of rpsT*::yfp-(rpsT*) translational fusions in relation to exponential growth rates of reconstructed rpsT alleles in the same rpsT mutants. All values are set relative to isogenic wild-type controls and represent the mean (±SD) of at least three independent experiments. (E) As in (D) but with rpsT*::yfp_(rpsTwt) fusions. (F) Correlation between the relative fluorescence of translational fusions rpsT*::yfp-(rpsT*) and rpsT*::yfp_(rpsTwt). The wild-type fusions have not been included in the calculations for the correlation coefficient.