Fig. 1.
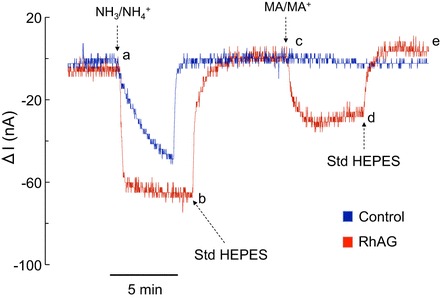
NH3/NH4+- and methyl amine/ammonium (MA/MA+)-induced currents (I) in H2O-injected and glycoprotein (RhAG)-expressing oocytes. All oocytes were clamped at −60 mV and exposed to standard HEPES-Ringer (Std HEPES), 5 mM NH4Cl HEPES-Ringer (NH3/NH4+), or 5 mM methylamine hydrochloride HEPES-Ringer (MA/MA+), pH 7.5, solution. In oocytes expressing RhAG (red tracing), an inward current was observed upon switching solution from standard HEPES to NH3/NH4+ (segment ab). Inward current recovered upon return to standard HEPES solution (segment bc). An inward current was also observed upon switching solution from standard HEPES to MA/MA+ (segment cd). Inward current also recovered upon return to standard HEPES solution (segment de). In H2O-injected oocytes (blue tracing), NH4+ influx caused an inward current (segment ab) that was not seen with MA+ (segment cd). Tracings are representative of results from 6 RhAG-expressing and for 10 H2O-injected oocytes.
