Fig. 9.
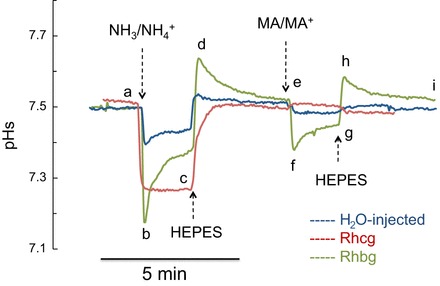
Changes in pHs induced by NH3/NH4+ and MA/MA+ in Rhbg-expressing, Rhcg-expressing, and H2O-injected oocytes. Exposure of oocytes to NH3/NH4+ (5 mM) caused a rapid decrease in pHs in Rhbg-expressing, Rhcg-expressing, and control oocytes (segment ab). In oocytes expressing Rhbg (green tracing) and control oocytes (blue tracing), decrease in pHs was followed by a spontaneous and partial recovery (segment bc), whereas in Rhcg-expressing oocytes (red tracing), pHs acidification was sustained. These changes were reversed upon removal of NH3/NH4+ from the bath (segment cde). MA/MA+ (5 mM) also caused a rapid and transient, but smaller, decrease in pHs in oocytes expressing Rhbg (segment efg, green tracing) but very little change in Rhcg-expressing (segment efg, red tracing) or control (segment efg, blue tracing) oocytes. Tracings are representative of results from 12 H2O-injected, 11 Rhbg-expressing, and 7 Rhcg-expressing oocytes.
