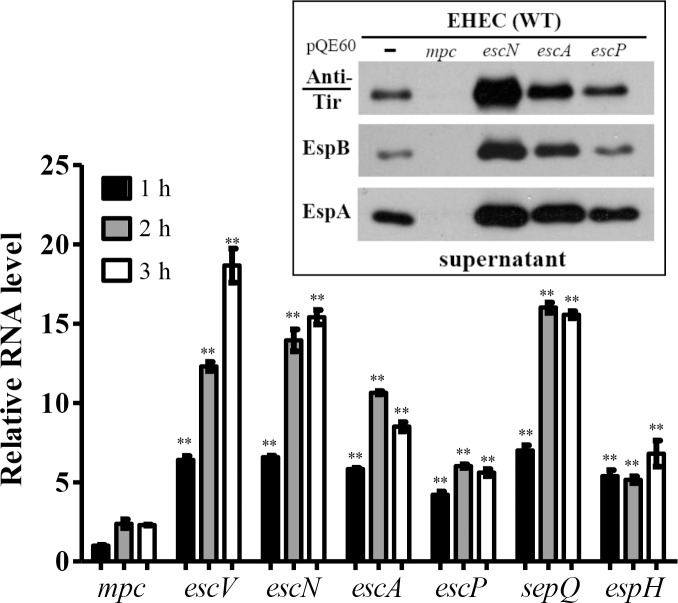
Fig 6. Real-time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to compare the levels of the RNA transcripts of the ORFs within lee3 during the process of T3SS activation.
EHEC cultivated in LB was switched to M9 in the presence of 5% CO2 in order to activate TTSS and then the bacteria were harvested at different time points. Total RNA was isolated, quality assured and then used for real-time RT-PCR. RNA levels were first normalized against the 16S rRNA present in the sample and then their relative amounts (as a fold increase) were calculated against the amount of mpc RNA transcript present when detected at hour 1. Experiments were carried out in triplicate, and the qRT-PCR result was further calibrated against the differences of the primer efficiency. Differently painted bars represent the mean values of relative RNA level of genes at different time points while error bars indicate the standard deviations. Student’s t test was applied to analyze the significance of the paired data, a comparison referenced accordingly to the measurement of mpc (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01). Note: two different scales are labeled in the Y-axis. Inset: protein secretion of TTSS is severely suppressed by over-expression of mpc but not by overexpression of escN, escA, or escP. The wild-type strain of EHEC was transformed individually with pQE60-based plasmids to drive target gene expression. After transformation, bacterial culture supernatants were harvested for Western blotting analysis in order to detect secreted Tir, EspB, and EspA by using specific antibodies separately. Over-expressed Mpc, EscN, EscA, and EscP present in the transformants were monitored by analyzing the target proteins present in the appropriate bacterial lysates (data not shown).