Fig. 1.
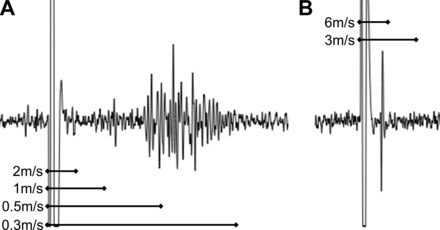
Electrically evoked compound potentials in vagal ganglia. Vagus nerve stimulated by concentric stimulating electrode, action potentials recorded extracellularly within the vagal sensory ganglia. Conduction velocities calculated from physical distance traveled divided by time separating shock artifact from electrical potentials. A: representative image showing the majority of sensory fibers are slowly conducting C fibers. B: rare example of more rapid A fiber (likely myelinated).
