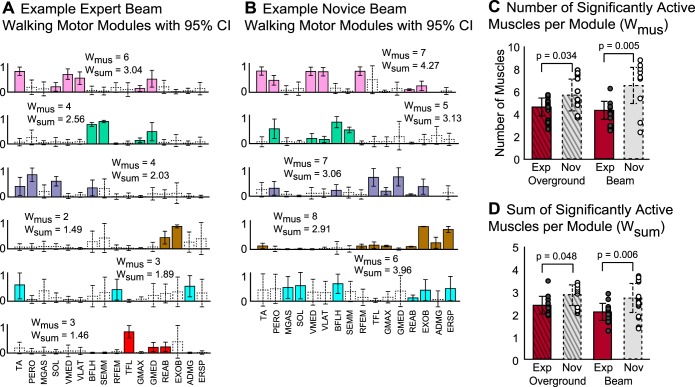
Fig. 7.
Motor module coactivity for experts and novices during overground and beam walking. A and B: example expert (A) and novice (B) motor modules. Coactivity was quantified as the average number of significantly active muscles per module (Wmus), as well as the average sum of those significantly active muscles per module (Wsum). Significantly active muscles (filled bars, solid border) represent those whose activation was consistently greater than zero, despite step-to-step variations. Muscles were classified as significantly active if their 95% CI did not include zero, whereas nonsignificantly active muscle (open bars, dashed border) had 95% CIs that included zero. C: Wmus was lower among experts (red bar, solid border) than novices (gray bar, dashed border) in overground and beam walking (overground: P = 0.034, beam: P = 0.005). Wmus did not differ between overground and beam walking for experts or novices. Average Wmus per subject is denoted by the circles (experts: gray-filled circles; novices, open circles). D: Wsum was also lower among experts compared with novices during overground and beam walking (overground: P = 0.048, beam: P = 0.006). In both experts and novices, Wsum did not differ between overground and beam walking. Values are means ± SD.