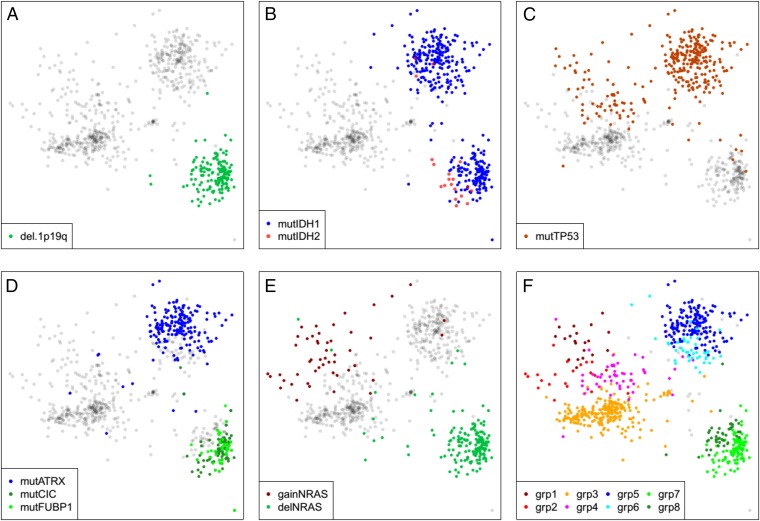
Fig. 2.
Genomic variations divide gliomas into eight distinct subtypes. (A) (1p,19q) codeletions occur exclusively in the Lower Right (oligo) cluster of samples. (B) IDH1 mutations occur in both astro and oligo LGG clusters, but most IDH2 mutations occur in the oligo CIMP-LGG cluster. (C) TP53 mutations are largely confined to the astro CIMP-LGG cluster and the diffuse portion of the non-CIMP cluster. (D) Mutations in ATRX primarily impact a subset of the astro cluster (Top Right), whereas CIC and FUBP1 mutations define a subset of the oligo cluster. (E) Heterozygous deletions and low-copy gains of NRAS mark the oligo cluster and a diffuse portion of the non-CIMP cluster. (F) Together, the genomic markers described in A–E define eight distinct tumor subtypes, as follows. Group1 = nonCIMP & gainNRAS & mutTP53. Group2 = nonCIMP & gainNRAS & wtTP53. Group3 = nonCIMP & wtNRAS & wtTP53. Group4 = nonCIMP & wtNRAS & mutTP53. Group5 = CIMP.LGG & not1p19q & mutATRX & mutTP53. Group6 = CIMP.LGG & not1p19q & wtATRX & mutTP53. Group7 = (CIMP.LGG & del.1p19q) & (mutCIC OR mutFUBP1). Group8 = CIMP.LGG & del.1p19q & wtCIC & wtFUBP1.