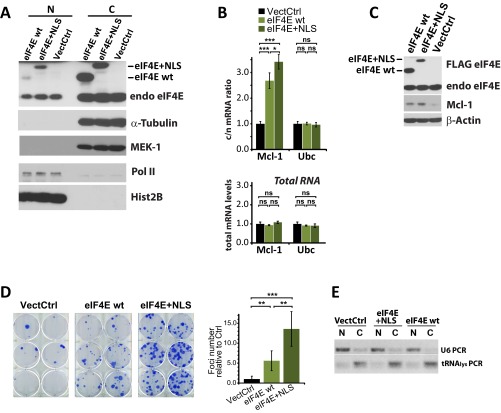
Fig. S5.
Effects of the addition of an NLS on eIF4E. (A) Fractionation analysis indicates that the eIF4E+NLS had increased nuclear levels relative to wild-type eIF4E (eIF4E wt). N and C indicate nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively. Tubulin and MEK-1 are fractionation controls for the cytoplasm, and Pol II and Hist2B (histone 2B) are fractionation controls for the nucleus. Note that eIF4E+NLS is expressed at lower levels than wild-type eIF4E (C). We note that confocal microscopy indicates there is more nuclear eIF4E than fractionation methods. These findings are similar to the findings by Lejbkowicz et al. (4), where eIF4E was more nuclear by confocal microscopy relative to fractionation results. There is an impression of less cytoplasmic eIF4E because it is distributed throughout the cytoplasm, as was quantified by Lejbkowicz et al. (4), but this observation did not completely account for the observed differences. This finding is true using many different antibodies, fixation conditions, etc. As suggested by Lejbkowicz et al. (4), it seems possible that eIF4E is released during the fractionation process (despite the fractionation controls indicating the fractions are intact), leading to an underestimation of the amount of nuclear eIF4E by this method. Under these circumstances, microscopy appears a more reliable method to assess the subcellular distribution of eIF4E. (B) mRNA export assays indicate that eIF4E+NLS increases export over wild type but only modestly, likely because of its reduced overall expression (C). (C) Western blot analysis indicates that eIF4E mRNA export targets are elevated in eIF4E+NLS relative to vector controls and wild-type eIF4E. Actin is provided as a loading control. (D) Anchorage-dependent foci assays for vector controls (VectCtrl), eIF4E wt, or eIF4E+NLS. Results are the foci number relative to vector controls reporting the mean and SD. (E) Fractionation controls for B. U6snRNA is a marker for the nucleus, and tRNA lysine is a marker for the cytoplasm. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.