Fig. 5.
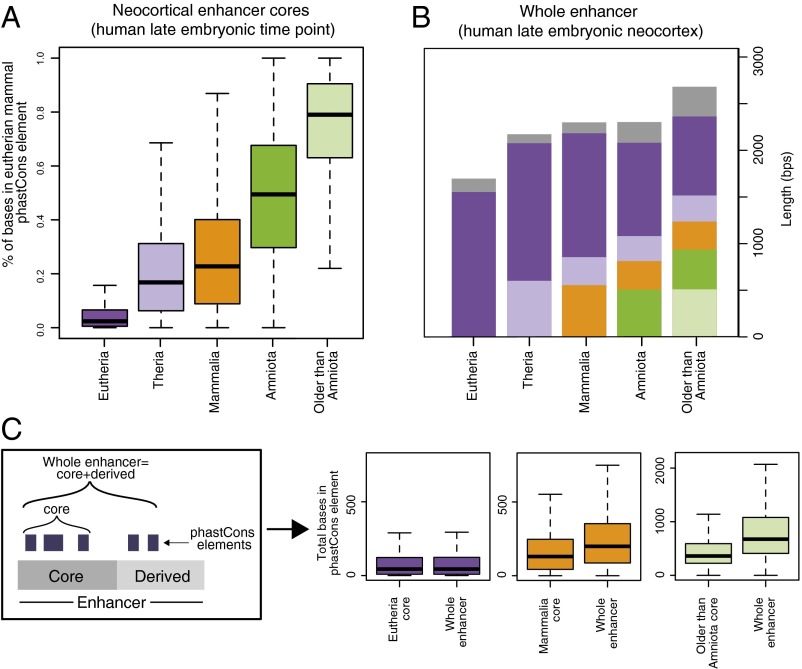
Older neocortical enhancers exhibit high sequence constraint and are composites of older and younger functional sequences. (A) Percentage of bases in neocortical enhancer cores from the human late embryonic time point that overlap a eutherian mammal phastCons conserved element. See also Fig. S4B. (B) Median lengths of H3K27ac enriched regions for neocortical enhancers from the human late embryonic time point. The evolutionary composition of enhancers is also indicated: The median core length is at the bottom of each bar, and median lengths of derived sequence segments are found above in different colors. Segment arrangement in the figure does not reflect the actual order of segments in enhancers—a variety of arrangements are observed in the data. Grey, younger than eutherian sequence; purple, eutherian-specific sequence; light purple, therian sequence; orange, mammalian sequence; green, amniote sequence; light green, older than amniote sequence. (C, Left) Schematic illustrating how constraint in the core was compared with that in the whole enhancer. (Right) The total number of bases that overlap eutherian mammal phastCons conserved elements in neocortical enhancer cores and whole enhancers.