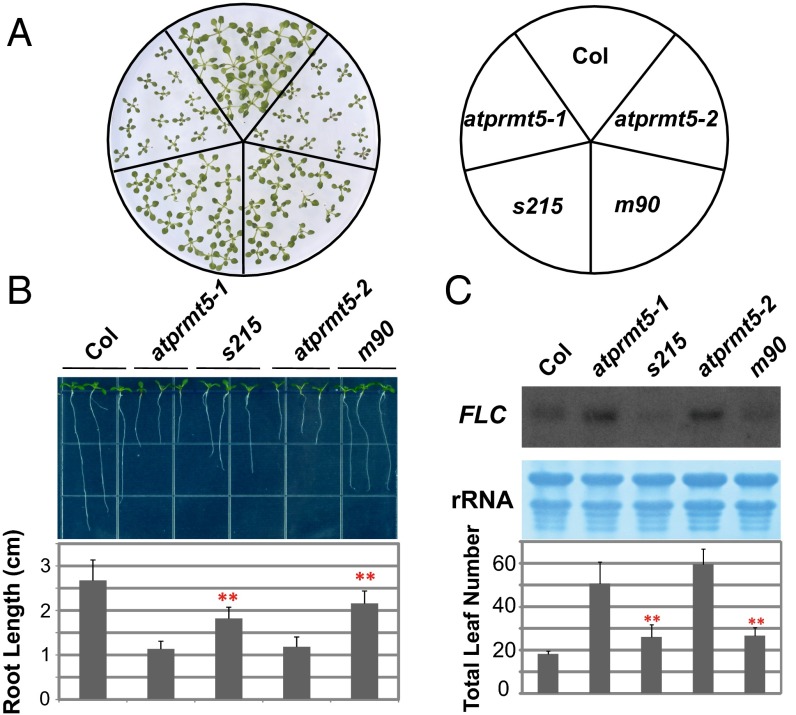
Fig. 1.
atprmt5 suppressors partially rescue the pleiotropic developmental defects of atprmt5 mutants. (A) Rescued growth retardation of young seedling leaves at 12 d. (B) Rescued primary roots of s215 and m90 at 9 d. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 20). Two-sided Student t test between atprmt5 and the suppressors was performed (**P < 0.01). (C) Rescued FLC expression and flowering time of s215 and m90. (Upper) The total RNAs from 12-d-old seedlings of Col, atprmt5, s215, and m90 plants were probed by RNA blot with the full-length coding sequence of FLC. rRNAs were used as a loading control. (Lower) Flowering time was assessed by total leaf number after plants stopped producing new leaves when plants were grown at 23 °C under long day conditions. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 30). Two-sided Student t test between atprmt5 and the suppressors was performed (**P < 0.01).