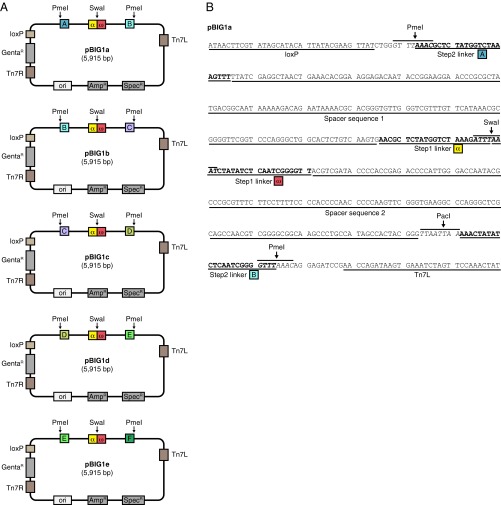
Fig. S3.
pBIG1 vectors. (A) Schematic representation of pBIG1 vectors. pBIG1 vectors can be maintained with Spectinomycin (SpecR resistance gene) or Ampicillin (AmpR resistance gene). For the selection in the first assembly step, Spectinomycin is used. Stocks of linearized pBIG1 cloning vectors are generated by SwaI digestion. This results in linear vector backbone with linker sequences α and ω at the fragment ends. After the first assembly step, the generated PGCs can be released from the vector backbone by PmeI digestion. The five pBIG1 vectors differ only in the linker sequences (A, B, C, D, E, and F) next to the PmeI sites as indicated. All biGBac vectors (pLIB, pBIG1, pBIG2) contain Tn7 elements (Tn7L, Tn7R) and a Gentamicin resistance gene (GentaR) for generation of baculoviruses and a LoxP site for compatibility with Multibac donor plasmids. (B) DNA sequence of pBIG1a shown from the LoxP site to Tn7L element. The positions of α, ω and A, B linker sequences as well as of the restriction sites SwaI, PmeI, and PacI are shown. The linker sequences of the first and the second assembly step are separated by spacer sequences (derived from HSVtk terminator sequence in pFL) to avoid interference of the two linker sequence sets in Gibson reactions.