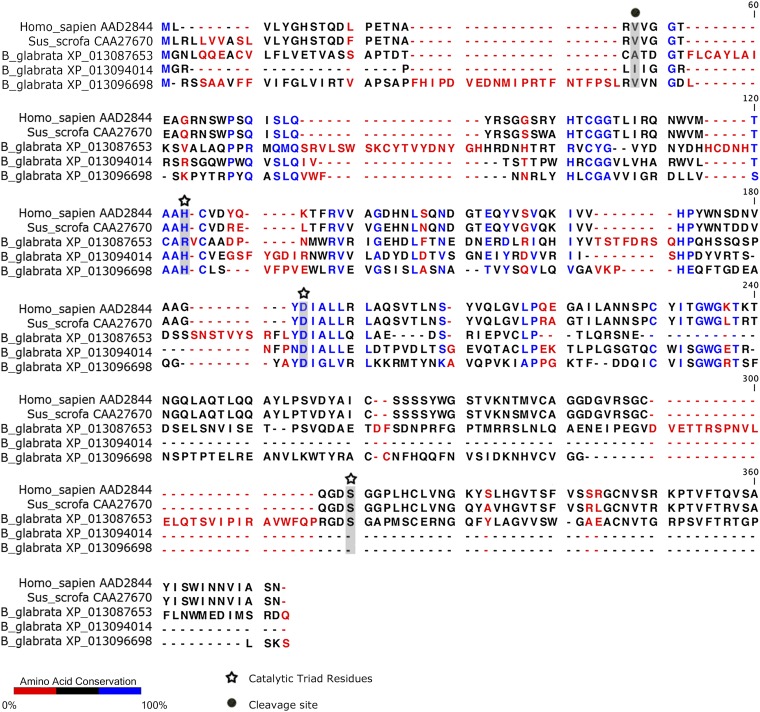
Fig. S10.
Amino acid alignment of human, porcine, and B. glabrata elastases. Analysis of the predicted amino acid sequence of B. glabrata elastase suggests that it possesses all relevant catalytic sites known to be active in human and porcine elastases. Only incomplete sequences were available for two of the three B. glabrata elastase variants, so the final catalytic residue could not be compared. Homo sapiens elastase (AAD2844.1), Sus scrofa elastase (CAA27670), and the three B. glabrata predicted elastase proteins (XP_013096698, XP_13094014, and XP_013087653) were aligned in CLC Genomics workbench using the alignment tool with a gap open cost of 10, a gap extension cost of 1.0, and an end gap cost of “as any other” using the very accurate (slow) option. The active sites were identified using the NCBI conserved domains database.