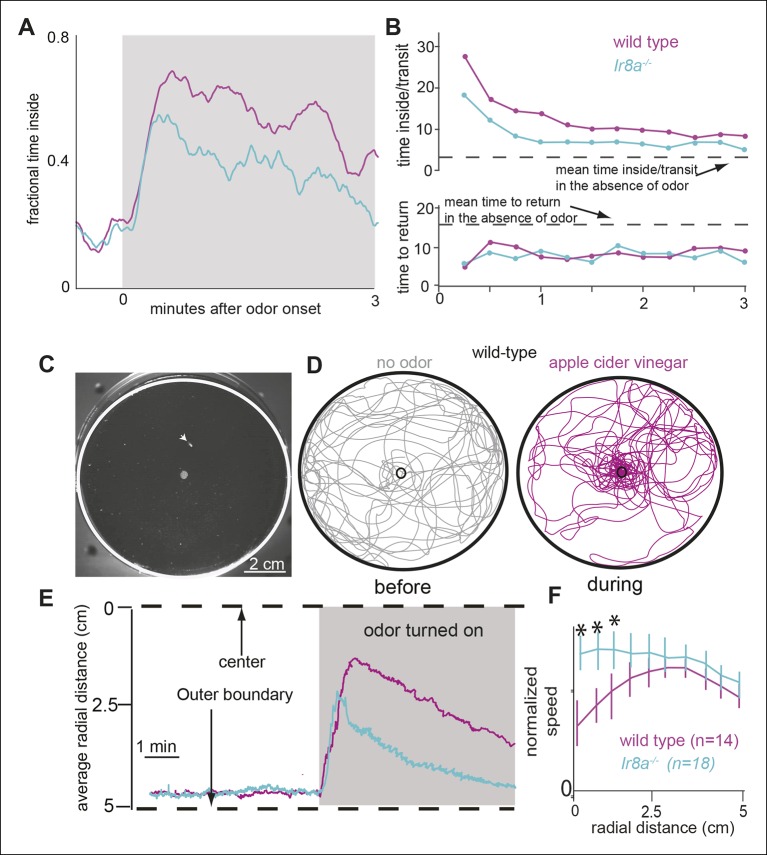
Figure 10. Ir8a mutants approach ACV at the same rate as wild-type but spend less time in proximity to it.
(A) Ir8a mutant find the odor as well as the wild-type flies but because they spend less time inside the odor-zone on each visit their attraction to odor decreases with time at a faster rate than wild-type flies. (B). The time a fly spends inside the odor-zone on a single visit decreases at a much slower rate for wild-type than for the Ir8a mutant. In contrast, the time a fly takes to return to the odor-zone is the same for both genotypes. (C) A photo of the arena with the outer edge marked with a white line. Fly can be seen as a tiny white object (marked with an arrowhead). The hole in the center is used to deliver odors. (D) Tracks of a control fly shows that it is strongly attracted to apple cider vinegar. (E) Radial density averaged over multiple flies show that Ir8a mutants find the odor as quickly as the wild-type but leave the odor much faster. (F) Speed (between 0-–2 min after odor on) near the odor source decreases in wild type but not in the Ir8a mutants.