Figure 2.
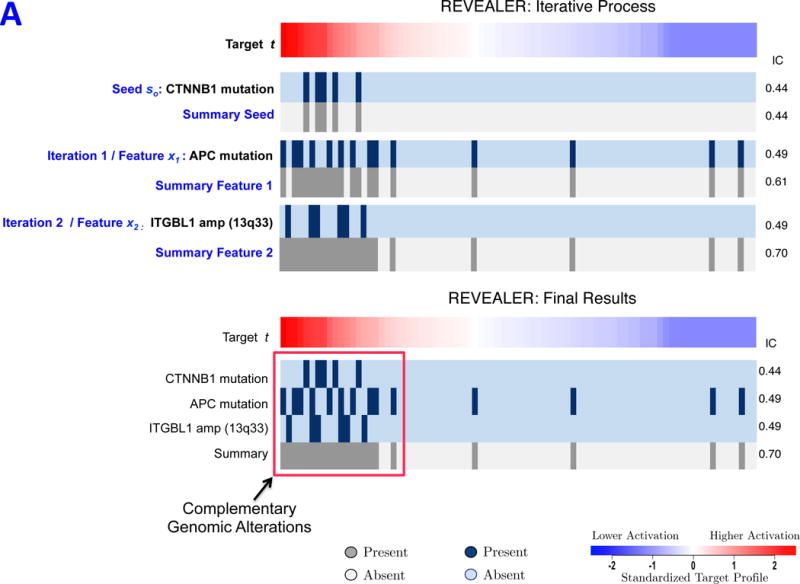
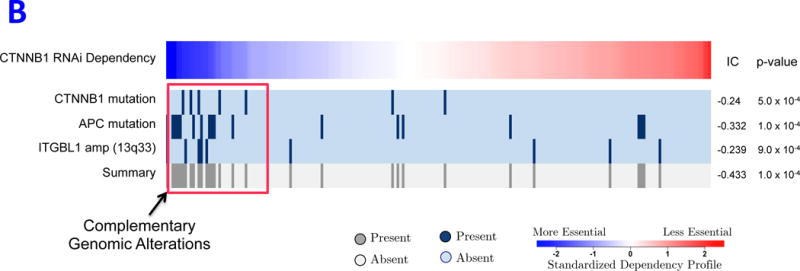
REVEALER results for transcriptional activation of β-catenin in cancer. A) This heatmap illustrates the use of the REVEALER approach to find complementary genomic alterations that match the transcriptional activation of β-catenin in cancer. The target profile is a TCF4 reporter that provides an estimate of the degree of activation of β-catenin. The “seed” is the β-catenin activating mutations, the known “cause” of high values in the target. REVEALER iterates two times and finds APC mutations and the amplification of 13q33 as complementary alterations. At the bottom the heatmap shows the complete set genomic alterations associated with activation of β-catenin found by REVEALER. As can be seen in the figure the features are highly complementary and account for 17 out of the top 20 samples with highest reporter values. B) Profiles of the features shown in Figure 2A, compared with an shRNA profile of β-catenin dependence in 209 cell lines (Supplementary Information). The 3 features are associated with a high degree of β-catenin essentiality but are also highly complementary to each other. The IC scores and nominal p-values with respect to the target are shown on the right side of the heatmap.
