Figure 1. Isolation of vaccine-induced NHP antigen-specific single cell and antigen-specific Ig heavy chain gene segment usage.
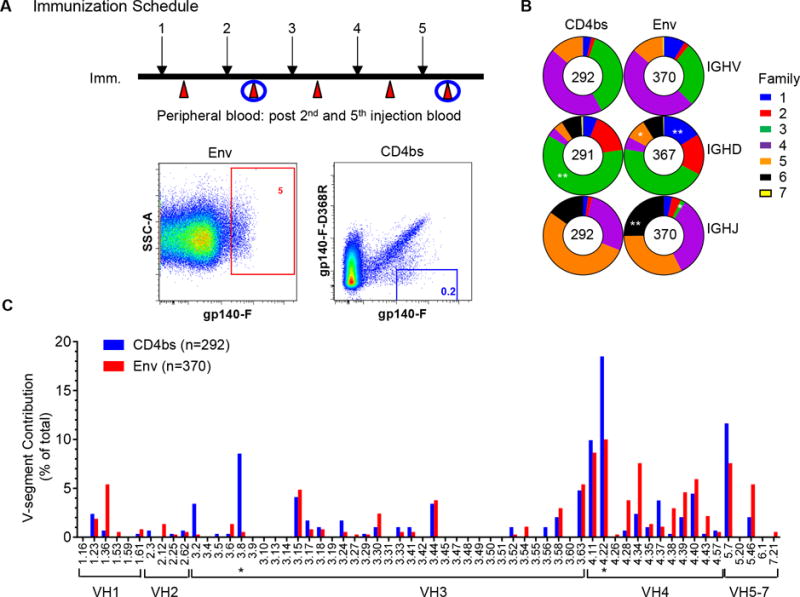
(A) Schematic presentation of the immunization schedule and antigen-specific B cell sorting. Upper panel, immunization/sampling schedule. Whole blood samples from two macaques inoculated with HIV Env YU2gp140-F trimer 5 times in a monthly interval (black arrow) were collected 1–3 weeks after each inoculation (red arrow) to prepare PBMCs (20). PBMCs from time points following the 2nd and 5th immunization (Imm 2 and Imm5) were subjected to single cell sorting, indicated with blue circles. Lower panel, single cell sorting for Env-and CD4bs-specific memory B cells. IgG memory B cells were defined as CD3−/CD8−/ Aqua Blue−/ CD14−/ CD20+/ IgG+/ CD27+/ IgM−. Env- and CD4bs-specific memory B cells were then gated by phenotype of gp140-Fhi and gp140-Fhi/gp140-F–D368Rlo, respectively. Gate frequency (percent) of Env- and CD4bs-specific memory B cells out of total memory B cells is depicted in red and blue, respectively. (B) IGHV-, D-, and J-family Ig-gene usage of sorted Env- and CD4bs-specific memory B cells, defined by IgBLAST and IMGT/High V-Quest. Heavy chain gene families are color coded, with size of the colored area corresponding to the frequency (percent) out of the total number of sequences indicated in the center of the graphs. Differences in the gene family usage between the Env- and CD4bs-specific Ig repertoires were evaluated using χ2 test with *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (C) Env- (red) and CD4bs (blue) -specific Ig repertoire V-gene segment contribution to the total number of sequences of each individual repertoire. VH3.8 and VH4.22, over-expressed in CD4bs-specific Ig repertoire, were marked with asterisk. Two-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis with *p<0.05.
