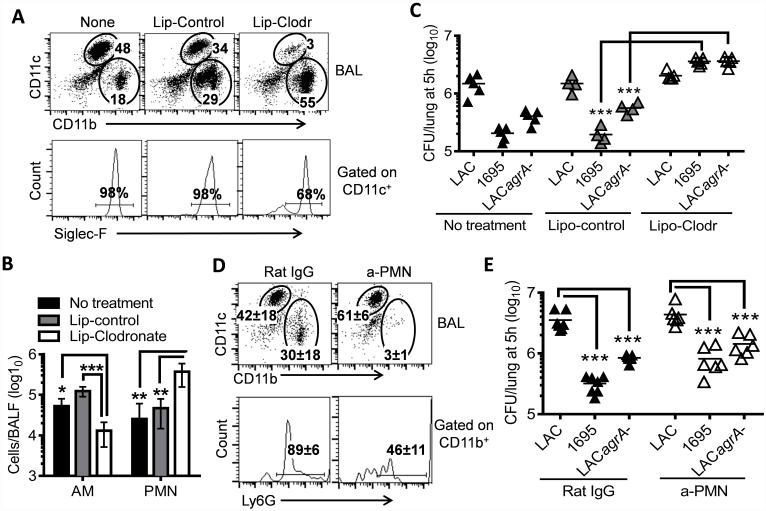
Figure 5. Alveolar macrophages are responsible for initial bacterial killing in the lower airways.
(A) Inflammatory cell profiles, (B) numbers of alveolar macrophages (AM) and neutrophils (PMN) in the airways (4~5 mice/group), and (C) numbers of bacteria in the lungs 5 h after infection of naïve, liposome-control or liposome-clodronate treated C57BL/6 mice with 107 CFU of LAC-JE2 WT, agrA mutant, and 1695 in a 1:1:1 mixture. Numbers (mean of 4~5 mice/group) shown in (A) represent percent of indicated populations in the respective gates. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. (D) Airway inflammatory cell profiles and (E) numbers of bacteria in the lungs 5 h after infection of α-PMN antibody-treated mice with 107 CFU of LAC-JE2 WT, agrA mutant and 1695 in a 1:1:1 mixture. Control mice were treated with Rat IgG. Data shown were combined from two independent experiments. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01 and ***P< 0.001, Tukey's multiple comparisons test.