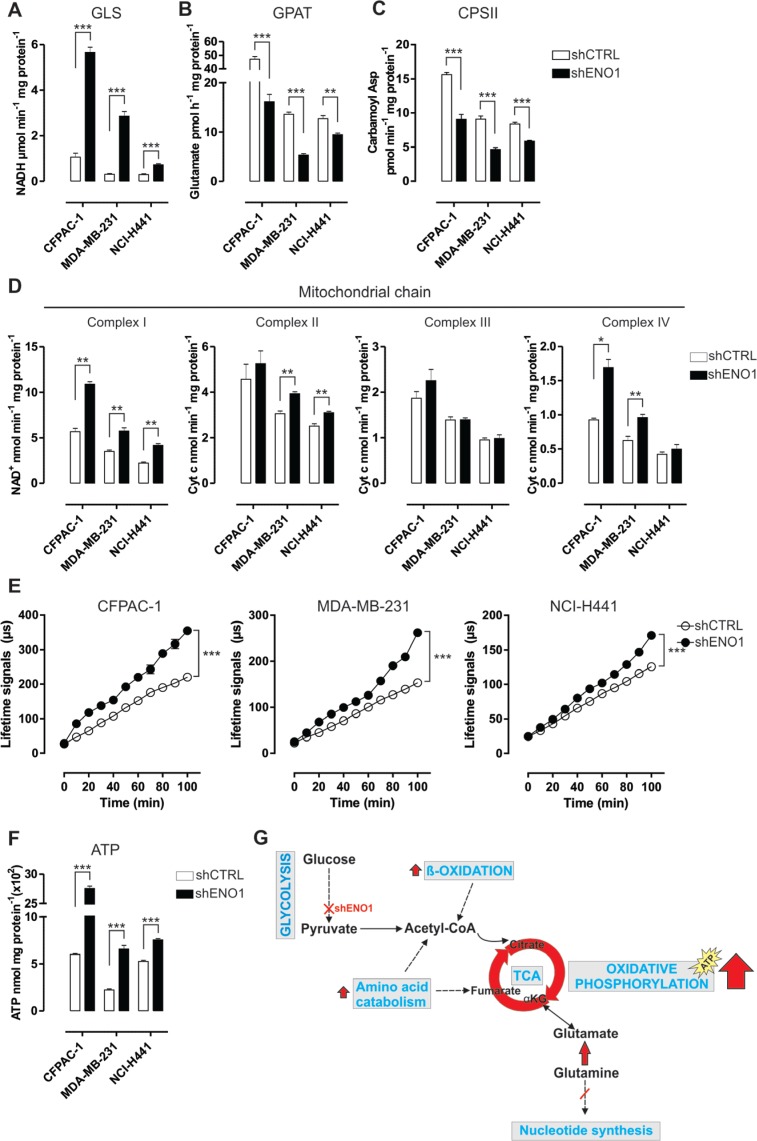
Figure 3. ENO1 silencing induces a decrease in nucleotide base synthesis and promotes oxidative phosphorylation.
A.–C. Analysis of glutaminase (GLS) (A), glutamine amidophosphoribosyltransferase (GPAT) (B) and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPSII) (C) activity in CFPAC-1, MDA-MB-231 and NCI-H441 cell lines transduced with shCTRL (white bars) or shENO1 (black bars). GLS activity is expressed as μmol NADH/min/mg protein. GPAT activity is an index of the de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides and is expressed as pmol glutamate/h/mg protein. CPSII activity is an index of the de novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides and is expressed as pmol carbamoyl aspartate/min/mg protein. D. Analysis of the activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I and complexes II-IV in CFPAC-1, MDA-MB-231 and NCI-H441 cell lines transduced with shCTRL (white bars) or shENO1 (black bars), expressed as nmol NAD+/min/mg mitochondrial protein for complex I, nmol Cyt c reduced/min/mg mitochondrial protein for complexes II-III, nmol Cyt c oxidized/min/mg mitochondrial protein for complex IV. E. Analysis of oxygen consumption in CFPAC-1, MDA-MB-231 and NCI-H441 cell lines transduced with shCTRL (white dots) or shENO1 (black dots). Results were expressed as the lifetime signal of the fluorescent probe MitoXpress provided in the kit versus the assay duration (μs). Curves were compared by two-way ANOVA, ***p < 0.001. F. Analysis of ATP production in CFPAC-1, MDA-MB-231 and NCI-H441 cell lines transduced with shCTRL (white bars) or shENO1 (black bars). All graphs illustrate the mean result of three independent experiments ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01;***p < 0.001 relative to shCTRL. G. Cartoon illustrating the catabolic pathway adaptations induced by ENO1 silencing. ENO1 silencing promotes fatty acid beta oxidation, which restores acetyl-CoA bulk and increases the TCA anaplerotic reactions derived from phenylalanine catabolism. These events, together with the increased entry of glutamine-derived metabolites into the TCA cycle, induce a decrease in nucleotide base synthesis and promote oxidative phosphorylation.