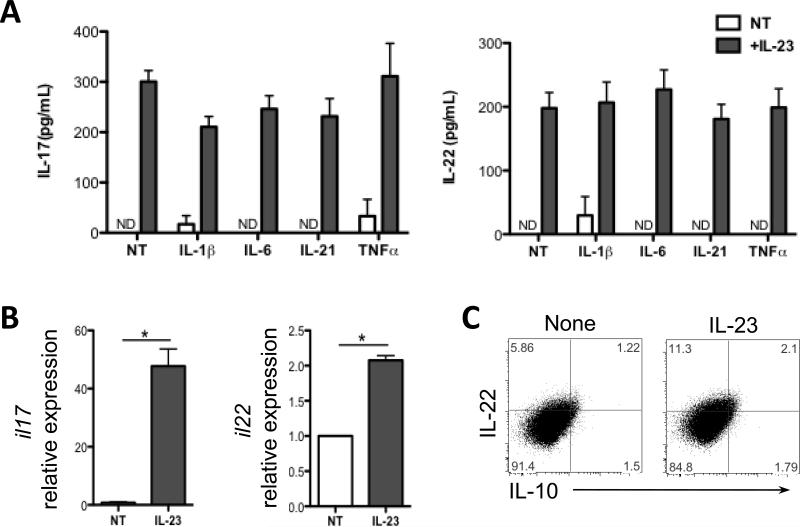
Figure 1. IL-23 stimulates neutrophil production of IL-17 and IL-22.
(A) Peritoneal neutrophils were treated with IL-1β (20ng/ml), IL-6 (30ng/ml), IL-21 (20ng/ml), or TNFα (20ng/ml), alone or in combination with IL-23 (20ng/ml) for 24 hours. IL-17 and IL-22 production were measured from the supernatant by ELISA. (B) Neutrophils were stimulated with IL-23 for 6 hrs. mRNA for il17 and il22 were determined by qRT-PCR and normalized against gapdh. The relative expression of IL-17 and IL-22 untreated neutrophils was arbitrarily set to 1.0. IL-17 and IL-22 expression was compared between the IL-23-treated and untreated neutrophils. *p<0.05. NT, no treatment. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. (C) Neutrophils were stimulated with IL-23 (20ng/ml) in the presence of Golgi Stop for 12 hours. Cytokine expression was measured by flow cytometry. FACS plots are representative of 3 independent experiments.