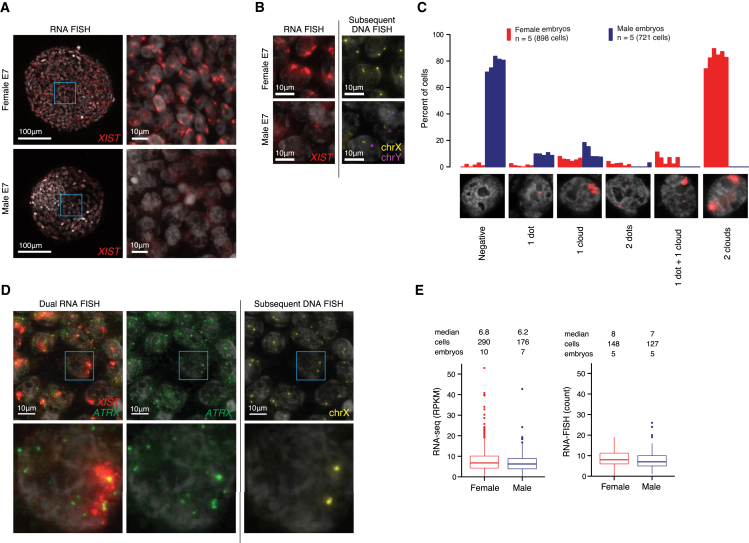
Figure 7.
Single-Molecule RNA-FISH Confirmed Biallelic Expression of XIST and ATRX
(A) Single-molecule RNA-FISH of XIST shown for a female and male E7 embryo. Zoomed-in regions (right) highlight that two XIST clouds (red) were observed in female nuclei (white, Hoechst-stained), but not in male.
(B) XIST clouds were localized at the X chromosomes (sex chromosomes were identified via DNA-FISH, staining chrX:p11.1–q11.1).
(C) Barplot with RNA-FISH XIST count statistics from 898 female cells (five embryos) and 721 male cells (five embryos), categorized by the XIST localization pattern observed in the nucleus.
(D) Left: single-molecule RNA-FISH of ATRX and XIST in a female E7 embryo. Two stronger ATRX speckles were typically observed within the nuclei, positioned at the XIST clouds. Right: DNA-FISH of chromosome X, indicating that the two stronger nuclear ATRX dots localized to the X chromosomes.
(E) Boxplots of E7 RNA-seq and RNA-FISH ATRX expression levels. RNA-FISH counts confirmed that the expression levels of ATRX in female and male were on par (mean 8.9 and 8.0; median 8 and 7, respectively), indicating dosage compensation at E7.