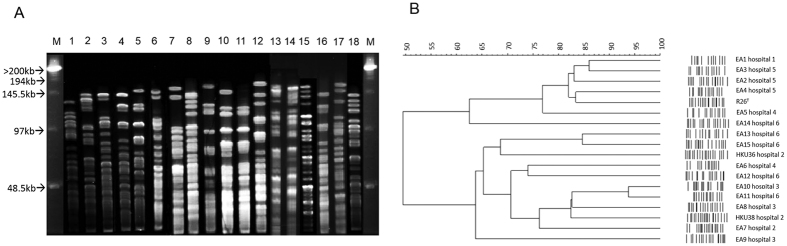
Figure 3. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) analysis of the 17 E. anophelis isolates and E. anophelis type strain R26T.
(lane 1 = EA1, lane 2 = EA2, lane 3 = EA3, lane 4 = EA4, lane 5 = EA5, lane 6 = EA6, lane 7 = EA7, lane 8 = EA8, lane 9 = EA9, lane 10 = EA10, lane 11 = EA11, lane 12 = EA12, lane 13 = EA13, lane 14 = EA14, lane 15 = EA15, lane 16 = HKU38, lane 17 = HKU36, lane 18 = R26T, M = lambda marker). In Panel (A), PFGE was performed using CHEF Mapper XA system (Bio-Rad) and restriction endonuclease XbaI. Results showed that the 17 isolates possessed distinct PFGE patterns. In Panel (B), dendrogram was constructed with PFGE data by similarity and clustering analysis using the Dice coefficient (1% tolerance and 0.5% optimization) and unweighted pair-group method using average linkages with GelCompar II.