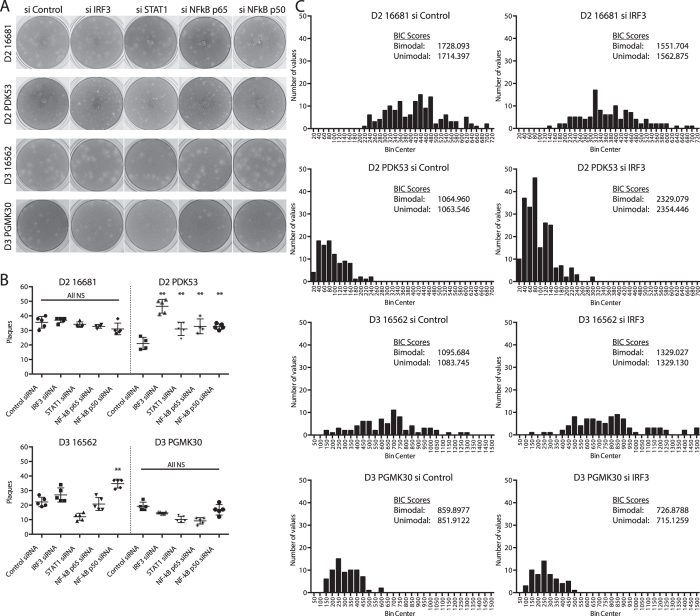
Figure 7. Effects of siRNA knockdown of antiviral activators on plaque size phenotype.
(A) Photographs of representative plaque assays for each of the DENV strains in cells transfected with either scrambled siRNA or siRNA that targed IRF3, STAT1 or NF-kB subunits. (B) Plaque counts (per well of a 24-well plate) for each of the DENV strains in cells transfected with either scrambled siRNA or siRNA that targed IRF3, STAT1 or NF-kB subunits. Significant increase in pfu was observed in PDK53 when inoculated onto cells transfected with IRF3, STAT1 or NF-kB knockdown. Significant increase in 16562 pfu was observed with NF-kB p50 knockdown. The other viruses and treatments showed no significant change. P-values were calculated using a two-tailed t-test; ** indicates p < 0.01. (C) Plaque size distributions of the four virus strains for control and IRF3 knockdown, along with corresponding Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) scores for unimodal or bimodal distribution. Lower BIC scores indicate better fit. All four control siRNA treatments yielded unimodal plaque size distributions. With IRF3 knockdown, PDK53 and 16681 plaques better fit a bimodal distribution, although the differences in plaque sizes were more distinct in PDK53. 16562 was neither more unimodal nor bimodal, whilst PGMK30 better fit a unimodal distribution.