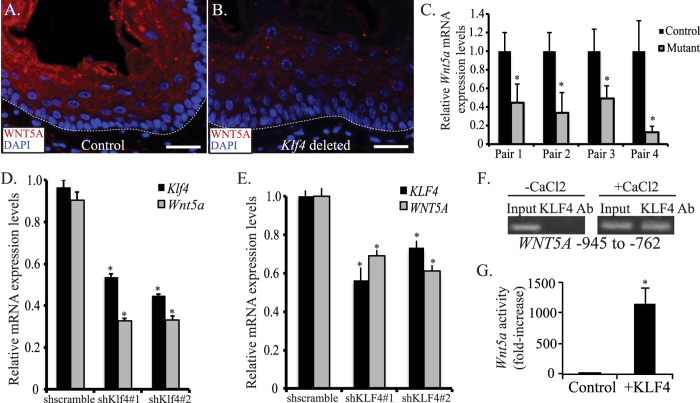
Figure 1. KLF4 transactivates WNT5A in esophageal epithelial cells.
(A,B) By immunofluorescence, control mice had extensive WNT5A staining (red) in the suprabasal and superficial layers of their esophageal epithelia (A). In contrast, WNT5A was nearly absent from esophageal epithelia of ED-L2/Cre;Klf4loxP/loxP mice (B). DAPI (blue) was used as a counterstain, and the white dashed line represents the approximate location of the basement membrane. Scale bars: 25 μM. (C) By quantitative real-time PCR, Wnt5a mRNA expression was decreased in the esophageal epithelium of each ED-L2/Cre;Klf4loxP/loxP mouse compared to its littermate control (*p < 0.05). (D) Klf4 knockdown in primary mouse esophageal keratinocytes in culture using either of two shRNA constructs resulted in a 57% decrease in Wnt5a mRNA levels by qPCR. (*p < 0.05) (E) In primary human esophageal keratinocytes, inducible KLF4 knockdown with either of two shRNA constructs led to a 31–39% decrease in WNT5A mRNA expression by qPCR. (*p < 0.05) (F) Right panel: When human primary esophageal keratinocytes were induced to differentiate with CaCl2, KLF4 bound to the region of WNT5A between −945 to −762 upstream of the transcriptional start site. Left panel: No KLF4 binding to WNT5A was observed in actively proliferating keratinocytes. Lack of binding at −1992 to −1796 (not shown) confirmed specificity. (G) Primary mouse esophageal keratinocytes transfected with pCDNA3-Flag-Klf4 to express Klf4 had an 1148-fold increase in luciferase reporter activity compared to cells transfected with pCDNA3.1 control. (*p < 0.05).