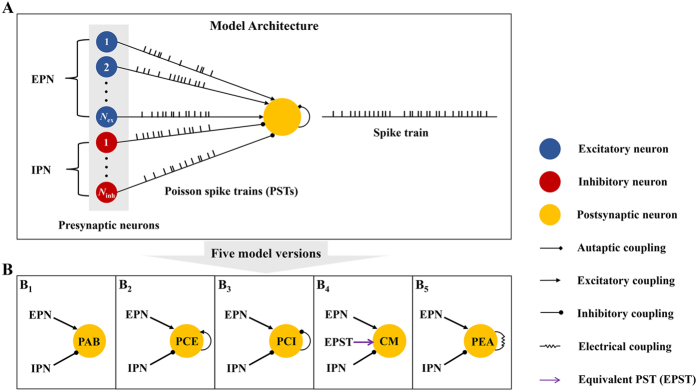
Figure 1. Schematic description of the computational model.
(A) Basic model architecture. In the model, the postsynaptic neuron receives balanced excitation-inhibition input from Nex excitatory presynaptic neurons (EPN) and Ninh inhibitory presynaptic neurons (IPN). For simplicity, each presynaptic neuron is modelled as a Poisson spike train generator, with a fixed input rate fin. In addition, the postsynaptic neuron is also driven by the self-feedback autaptic input from itself. (B) Five model versions used in our simulations. From (B1)–(B5), five models are termed as: the postsynaptic neuron with autapse blockade (PAB), the postsynaptic neuron with chemical excitatory autapse (PCE), the postsynaptic neuron with chemical inhibitory autapse (PCI), the comparative model (CM), and the postsynaptic neuron with electrical autapse (PEA), respectively. Note that the CM model is designed to compare with either the PCE or PCI model, in which the chemical autapse is replaced by an equivalent Poisson spike train (EPST) with both the same coupling type and firing rate.