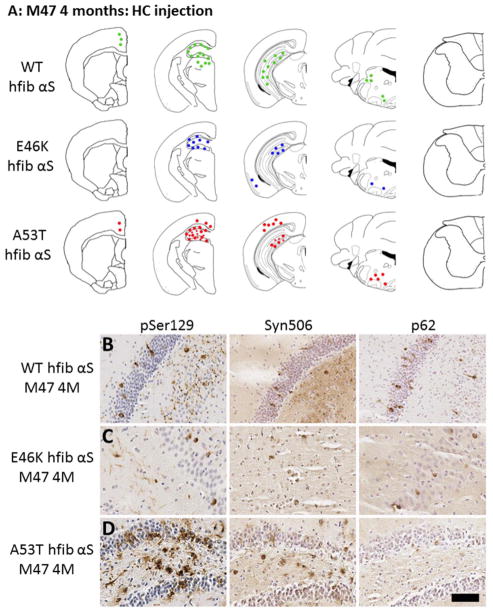
Fig 4. Induction of αS induction pathology in M47 Tg mice following hippocampal injection of wild-type, E46K, or A53T hfib αS.
(A) Schematic summary of αS pathology distribution at 4 months post intrahippocampal injection of wild-type 21–140 (WT), or full-length E46K or A53T hfib αS in M47 Tg mice. Diagrams show rostral/caudal distribution of αS pathology in M47 Tg mice. Tissue sections were stained with pSer129 and Syn506 to detect αS pathology. (B–D) Immunohistochemistry showing similar αS pathology induced by intrahippocampal injection of WT, E46K, or A53T hfib αS in M47 Tg mice at 4 months post-injection. Brain tissue sections with representative regions of the hippocampus surrounding the injection site in M47 Tg mice injected with WT (B), E46K (C), or A53T (D) hfib αS show rounded, perinuclear inclusions and neuritic pathology regardless of the type of inoculum detected with pSer129/81A antibody. Inclusions were also recognized by Syn506, a mouse monoclonal antibody that conformationally recognizes αS inclusions, and p62, a rabbit polyclonal antibody that non-specifically recognizes protein aggregates. Tissue sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. Scale bar = 50 μm.