Fig. 1.
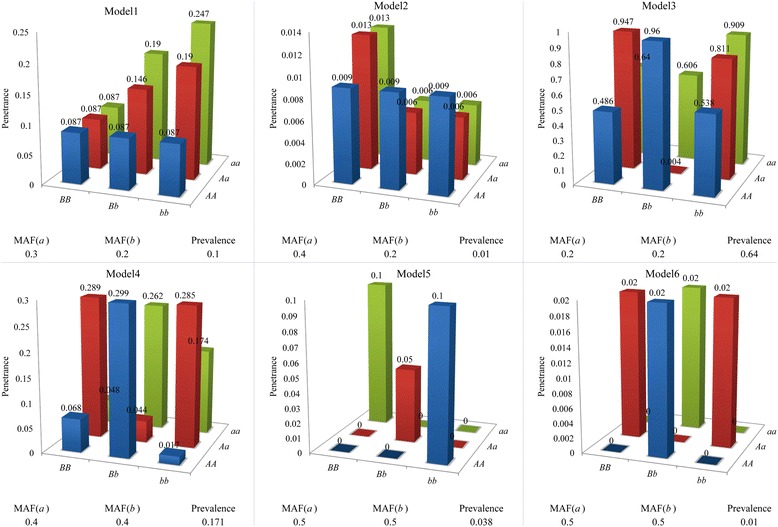
Six models of epistatic interactions. Model1 and Model2 are models displaying both marginal effects and interaction effects, and Model3 ~ Model6 show no marginal effects but interaction effects. Specifically, the penetrance in Model1 increases only when both SNPs have at least one minor allele [19, 20]; Model2 assumes that the minor allele in one SNP has the marginal effect, however, the effect is inversed while minor alleles in both SNPs are present [19]; Model3 and Model4 are directly cited from the reference [55]; Model5 is a ZZ model [56]; and Model6 is an XOR model [55]. Penetrance is the probability of the occurrence of a disease given a particular genotype. Prevalence is the proportion of individuals that have a disease. MAF(a) and MAF(b) are minor allele frequencies of a and b
