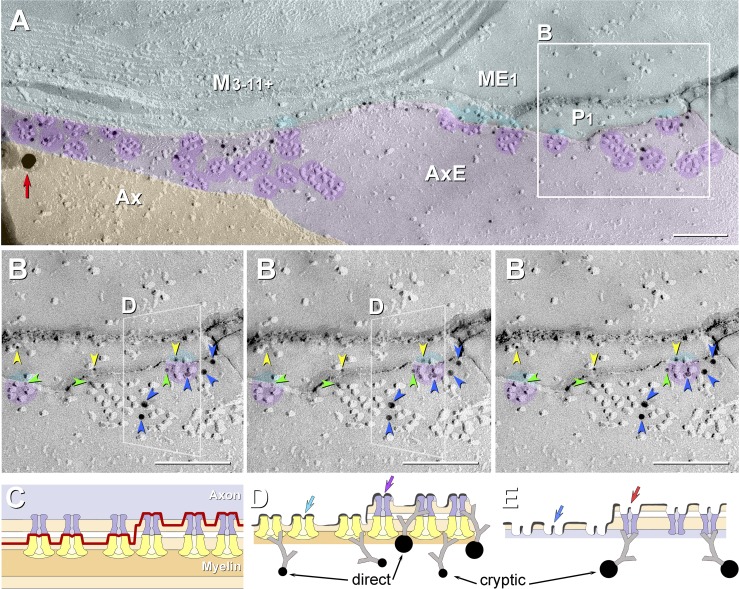
Fig. 9.
High-magnification FRIL images (A and B) and correlative diagrams (C–E) showing molecular coalignment of immunogold-labeled KV1 and Cx29 channels along the juxtamesaxonal axolemma/juxtamesaxonal innermost myelin (JMAX/JMIM). A: rosettes of axonal E-face particles (purple overlays) are labeled by ∼15 10-nm gold beads and by one 30-nm gold bead (red arrow at left edge). At the step from axolemmal E-face to myelin P-face, both proteins remain adsorbed following SDS washing, as inferred from presence of labels for both KV1 and Cx29. Ax, axoplasm (orange overlay); AxE, axolemmal E-face (light purple overlay); P1, innermost myelin P-face; ME1 and M3-11+, succeeding layers of myelin (light aqua overlay). B: stereoscopic (left pair of images) and reverse stereoscopic images (right pair of images) from boxed area in A, revealing “direct” labeling of Cx29 (yellow arrowheads) and KV1.1 IMPs (blue arrowheads) vs. “cryptic” labeling for Cx29 (green arrowheads) beneath KV1.1 rosettes. In reverse stereo, gold beads appear to be on top of the replica, making them easier to discern. Where the fracture plane stepped from axonal E-face to myelin P-face within a rosette (left and right sides of B), axonal E-face particles form one side of the rosette (purple portions of circular overlays), and underlying myelin P-face particles complete the rosette pattern (aqua portions of same circular overlays). The fracture step in box D is diagrammed as Fig. 10D. C–E: diagrams showing complementarity of composite KV1.1/Cx29 particles and their respective pits, with the icy pegs (E; arrows) corresponding to the central dimple (mouth of ion channel) in each IMP (D; arrows). C: diagram of fracture plane (red line) in B. D and E: complementary fracture faces. Unreplicated proteins remain attached to the replicated IMPs, allowing cryptic labeling (Fujimoto 1995, 1997; Rash and Yasumura 1999). Axonal E-face particles (blue channels) directly appose myelin P-face particles (yellow channels). Direct labeling occurs where the target protein is visualized by replication with platinum-carbon, whereas cryptic labeling occurs where the target protein is not visualized by replication but, nonetheless, is inferred on the basis of immunogold labeling of its strongly bound and platinum-replicated coupling partner. Thus some axonal E-face particles appear to be labeled for both KV1 and Cx29. Y-shaped gray linkers are primary and secondary antibodies. Scale bars, 0.1 μm.