Figure 3. Hsp70 required for polymerase NS5 biogenesis and function.
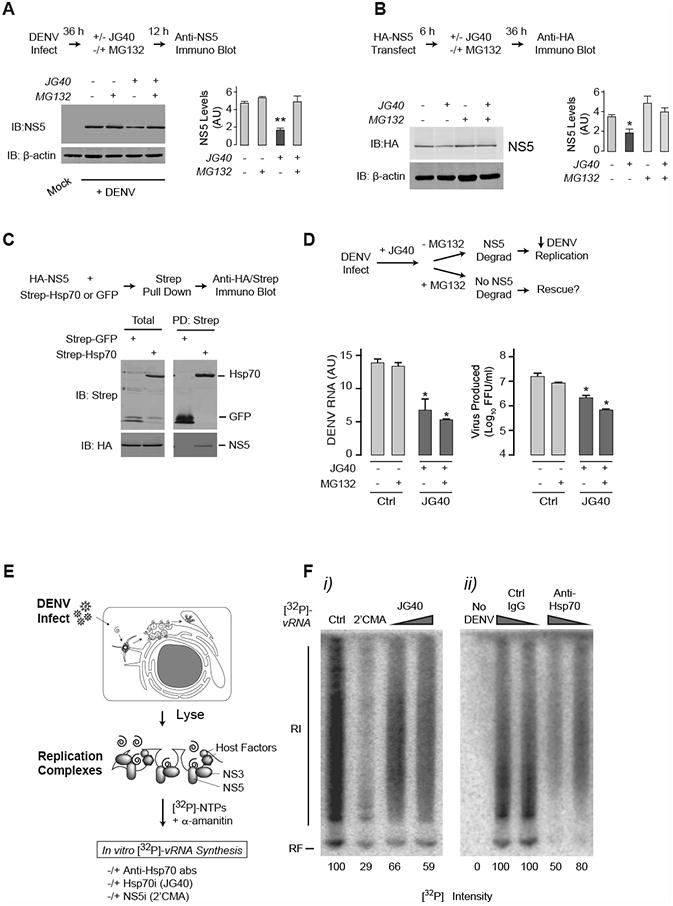
(A) Hsp70 inhibition leads to proteasomal degradation of NS5. Huh7 cells were infected with DENV2 at MOI 0.5. At 36 hpi, JG40 was added with or without proteasome inhibitor MG132 for an additional 12 h. Immunoblot analysis (left panel) and quantification (right panel) show that JG40-induced NS5 decrease is rescued by MG132.
(B) Hsp70 inhibition directly leads to proteasomal degradation of NS5. 293T cells transfected with HA-NS5 were treated with JG40 with or without proteasome inhibitor MG132 for 36 h and analyzed as in (A).
(C) Hsp70 physically associates with NS5. Strep-tagged Hsp70 or a GFP control were expressed together with HA-tagged NS5 in 293T cells, and their association assessed by coimmunoprecipitation and immunoblot. Total: represents 20% of the IP input.
(D) Rescue of NS5 levels by MG132 is not enough to restore DENV RNA replication and viral progeny production. NS5 degradation was blocked as in Fig. 3A, and levels of intracellular viral RNA and extracellular virus production measured by qRT-PCR (left panel) and FFA (right panel) respectively.
(A, B and C) Data is expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. * P < 0.05. ** P < 0.01
(E) In vitro RNA replication assay to test the effect of Hsp70 inhibition on activity of preassembled, folded DENV replication complexes. Crude replication complexes were harvested from infected cells 48 hpi, and processed as described.
(F) Hsp70 is required for NS5 polymerase activity. [32P]-vRNA synthesized in vitro in isolated replication complexes in the presence of NS5 or Hsp70 inhibitors (i) or following addition of control or anti-Hsp70 antibody (ii). No vRNA is synthesized in extracts from uninfected cells. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments.
