Fig. 1.
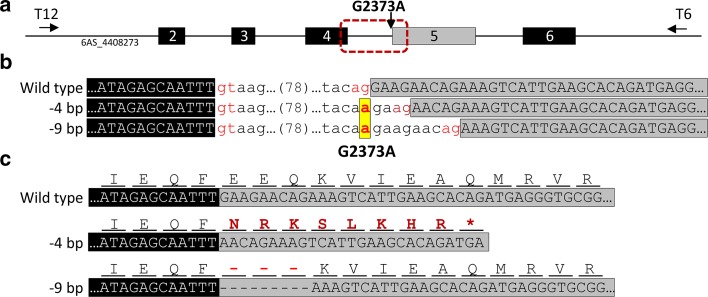
G2373A results in mis-splicing of TaGW2-A1. a Diagram of TaGW2-A1 target region including exons 2–6 (black and grey numbered boxes) and introns (thin line). The position of the G>A transition at position 2373 (G2373A) of IWGSC_CSS_6AS_scaff_4408273 is indicated. b Sequence alignment of gDNA from wild type (top) and mutant line T4-2235 (middle and bottom) which includes the G2373A transition. The G2373A mutation in line T4-2235 is in red font and yellow highlight. Exon sequences are in uppercase letters (exon 4 in black; exon 5 in grey), whereas intron sequences adjacent to the splice sites (red font) are in lowercase. The 78-bp of intron four are represented by the number 78 between parentheses. Note that the mutation leads to a change in the AG splice acceptor site in T4-2235 which removes either four bp (GAAG) or nine bp (GAAGAACAG) from exon 5. c Nucleotide sequence of cDNA spanning exons 4 and 5 in wild type (top sequence) and the two variants of mutant T4-2235 (middle and bottom sequences), with their corresponding amino acid translations. The −4 bp mutant allele is missing four nucleotides which disrupts the reading frame (red amino acid residues) leading to a premature termination codon (red asterisk) in the T4-2235 sequence. The −9 bp mutant allele is missing nine nucleotides which leads to the loss of three amino acids (EEQ) from the mutant protein