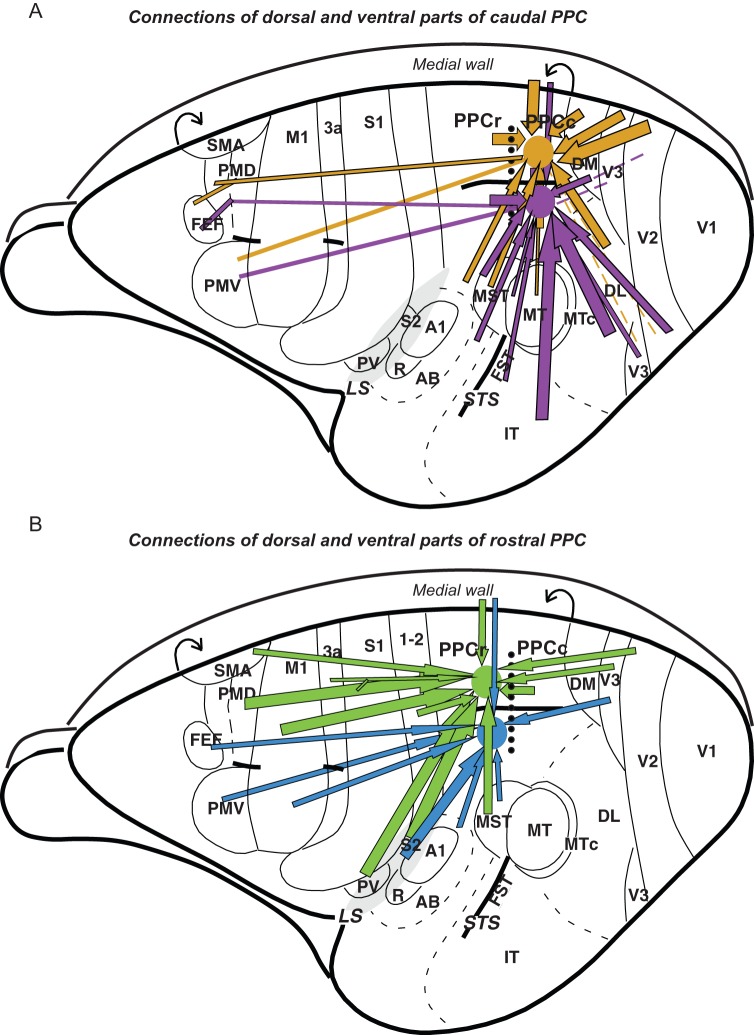
Figure 12.
A summary of the PPC connections in galago. Major connections of the caudal (A) and rostral (B) PPC marked with arrows are shown on the schematic dorsolateral views of the left hemisphere. The border between responsive to electrical stimulation PPCr and unresponsive PPCc is marked with dotted line. Cortical connections to dorsal and ventral regions of caudal PPC are marked with gold and violet arrows, respectively, and connections to dorsal and ventral PPCr are marked with green and blue arrows. Thick arrows represent strong connections and thin arrows represent weak connections. Note that major input to PPCc comes from visual areas and to PPCr from somatosensory and motor areas. Rough topography of PPCc connections indicates that dorsal PPCc is connected strongly to dorsal parts of extrastriate cortex and ventral PPCc is connected to ventral parts of extrastriate cortex. Although visual input, especially from V3d, reaches PPCr directly, it is limited to the caudal PPC areas representing reaching and defensive behavior. Major visual information is sent to PPCr indirectly, via PPCc, as PPCc and PPCr are interconnected. Both PPCc and PPCr have connections with motor areas of frontal cortex, although these connections are denser for PPCr.