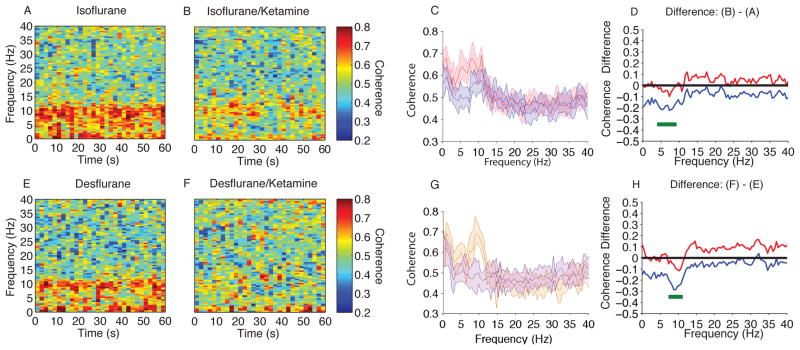
Figure 5.
Coherence comparison (F7–F8) of MDDE vs MDDE/Ketamine. (A, B) Median frontal coherograms of isoflurane- and isoflurane/ketamine-induced unconsciousness (n = 10; between subject comparison). (C) Overlay of median isoflurane/ketamine-induced unconsciousness coherence (blue), and median isoflurane-induced unconsciousness coherence (red). Bootstrapped median coherences are presented and the shaded regions represent the 95% confidence interval for the uncertainty around each median coherence. (D) The upper (red) and lower (blue) represent the bootstrapped 95% confidence interval bounds for the difference between coherence shown in panel C. During isoflurane-induced unconsciousness, there is significantly increased coherence between 3.91–9.28 Hz. (E, F) Median frontal coherograms of Desflurane- and Deflurane/ketamine-induced unconsciousness (n = 9; between subject comparison). (G) Overlay of median desflurane coherence (orange), and median isoflurane/ketamine-general anesthesia induced spectrogram (purple). Bootstrapped median coherences are presented and the shaded regions represent the 95% confidence interval for the uncertainty around each median coherence. (H) The upper (red) and lower (blue) represent the bootstrapped 95% confidence interval bounds for the difference between coherence shown in panel G. During isoflurane/ketamine-induced unconsciousness, there is significantly increased coherence between 7.32 – 11.23 Hz.
B, decibel; Hz, hertz; MDDE, modern day derivatives of ether; s, seconds. Horizontal solid green lines represent frequency ranges at which significant difference existed.