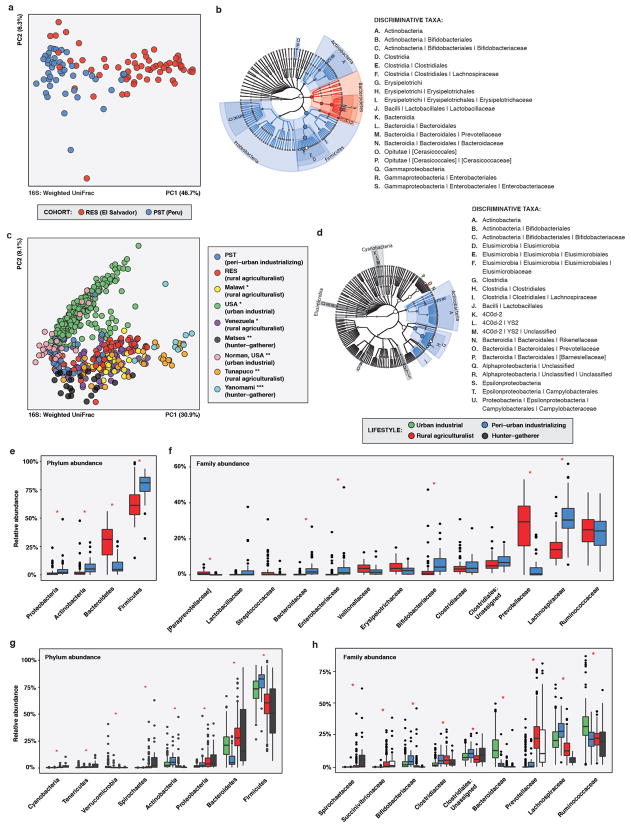
Extended Data Figure 3.
Phylogenetic composition of RES and PST human fecal microbiota and published microbiota from previous studies 14,19,25.
a, b, e, f, RES vs. PST. (RES n = 60, PST n = 45) c, d, g, h, RES and PST vs. published human microbiota. (RES n = 60, PST n = 46, other n = 446; see Supplementary Table 14) a, PCoA of weighted UniFrac distances between RES and PST human fecal microbiota, colored by cohort. Adonis R2 = 29.7%, p < 0.001. b, Taxa discriminating between RES and PST human fecal microbiota as determined by LEfSe. The phylogenetic tree includes all kingdom- to family-level taxa present in any sample. Colored taxa are discriminative between cohorts and have an LDA effect size of ≥ 4.0; they are colored by the cohort in which they have the highest abundance. Circle size is relative to the highest abundance in either cohort. c, PCoA of weighted UniFrac distances between RES and PST human fecal microbiota and published human fecal microbiota, colored by cohort. Cohorts are labeled by lifestyle and study (*19, **35, ***14). Adonis R2 = 37.6%, p < 0.001. d, Taxa discriminating between host lifestyles for RES and PST and published human fecal microbiota as determined by LEfSe, effect size threshold 3.0. Discriminative taxa are colored by the host lifestyle in which they are most abundant. e-f, Relative abundances of microbial e, phyla and f, families in human fecal microbiota from RES and PST. * p<0.05, Wilcox test with Bonferroni correction. g-h, Relative abundances of microbial g, phyla and h, families in human fecal microbiota from RES and PST and published human fecal microbiota, by lifestyle. * p<0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test with Bonferroni correction. e-h, Only taxa with a mean relative abundance of ≥1% in one cohort/lifestyle are shown. Taxa are in order of increasing overall mean relative abundance. Error bars = s.d., center bars = median.