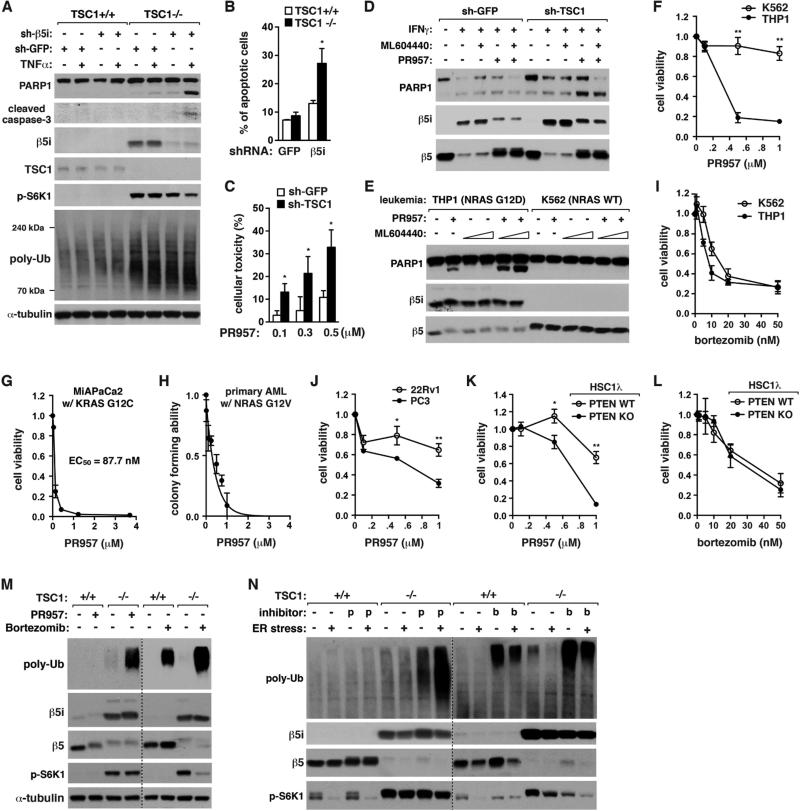
Figure 5. I-proteasomes are important for viability of mTORC1 hyperactive cells.
(A) β5i KD induces apoptosis and enhances accumulation of poly-Ub proteins in TSC1−/− MEFs but not TSC1+/+ MEFs. Cells were treated with TNFα (20 ng/ml) for 6 h.
(B) β5i KD enhances apoptosis to a significantly greater extent when TSC1 is deficient. MEFs treated with TNFα (20 ng/ml) for 24 h were stained with Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide and analyzed by FACS.
(C) Toxic effect of PR957 (48 h) is significantly increased when TSC1 is silenced in T24 cells. MTT assay was conducted for cell viability.
(D) I-proteasome inhibition induces PARP1 cleavage to a greater extent when TSC1 is silenced in T24 cells. Cells were treated with IFNγ (50 ng/mL), ML604440 (500 nM) and/or PR957 (100 nM) for 72 h.
(E) I-proteasome inhibition induces apoptosis for THP1 cells but not K562 cells. The leukemia cells were treated with PR957 (100 nM) and/or ML604440 (100 nM or 500 nM) for 24 h.
(F) PR957 (4 days) induces cell death for THP1 cells but not for K562 cells. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay.
(G) MIAPaCa2 pancreatic cancer cells are highly sensitive to PR957 (2 days) for cell viability.
(H) PR957 suppresses self-renewal capacity of primary leukemia cells from AML mice.
(I) Bortezomib (2 days) induces cell death to similar extents between K562 and THP1 cells.
(J) PC3 cells are more sensitive to PR957 (3 days) than 22Rv1 cells for viability.
(K) PTEN KO sensitizes HSC1λ cells to PR957 (24 h) for viability.
(L) Bortezomib (48 h) induces HSC1λ cell death regardless of PTEN status.
(M, N) PR957, but not bortezomib, has a selective effect on TSC1−/− MEFs for accumulation of poly-Ub proteins. Cells were treated with IFNγ (50 ng/mL) for 72 h, then PR957 (100 nM) or bortzomib (10 nM) for additional 24 h in the presence or absence of tunicamycin (10 μM), an ER stress inducer.
For every graph in Figure 5, values are means ± SD (*, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; n=3).
See also Figure S5.