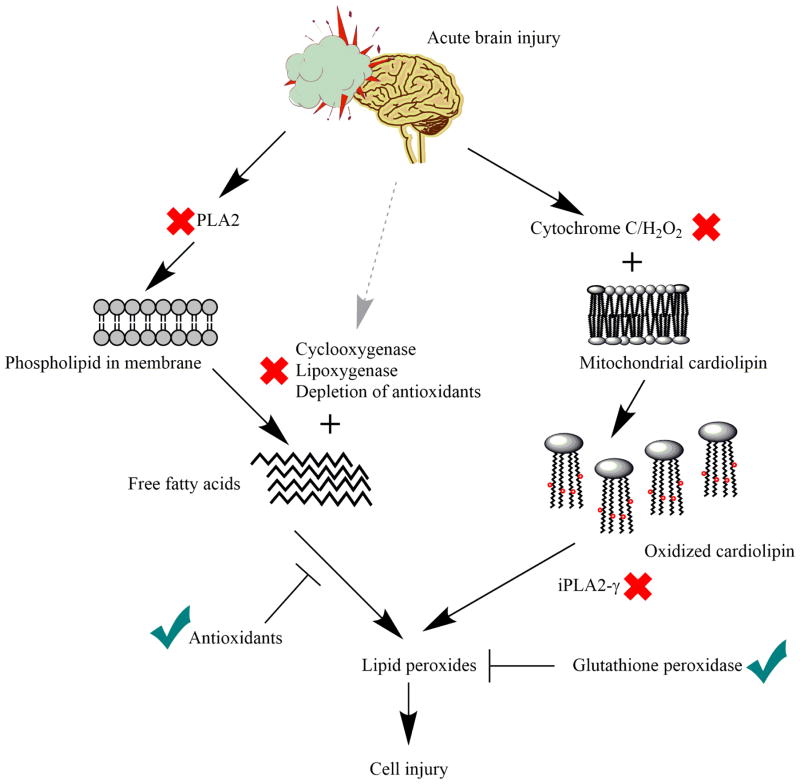
Figure 5. Lipid peroxidation mechanisms after TBI and possible therapeutic targets.
Lipid peroxidation after TBI follows two main pathways: 1) Calcium-dependent pathway in which PUFAs are initially hydrolyzed from phospholipids by PLA2 and subsequently oxidized by various enzymes; 2) Calcium-independent mitochondrial pathway in which mitochondria specific phospholipid cardiolipin is oxidized by cytochrome c/H2O2 and further hydrolyzed by calcium independent PLA2 to form lipid peroxides. Inhibition or reduction of marked components or enhanced activity of marked components in lipid peroxidation pathways are possible therapeutic options after TBI.