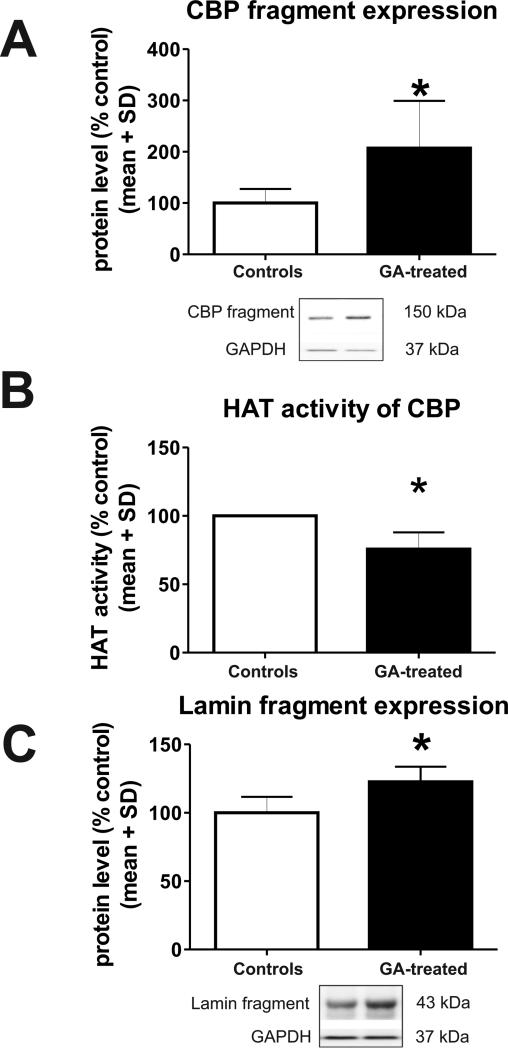
Figure 4. Anesthesia causes significant post-translational changes in cAMP-responsive element binding protein (CBP) in the immature hippocampus.
(A) Anesthesia induces significant increase in the 148 kDa CBP in the developing hippocampus at 24 h as compared with age- matched controls (n=6; *, p=0.021) suggestive of enhanced fragmentation. (B) Anesthesia causes significant decrease in CBP histone acetylase (HAT) activity at 24 h (*, p=0.026) in developing hippocampus as compared with age-matched controls (n=3). (C) Anesthesia causes significant increase in the expression of fragmented lamin (41-50 kDa), a chromatin organization component and well-known substrate of activated caspase-6 (n=4, *, p=0.029).