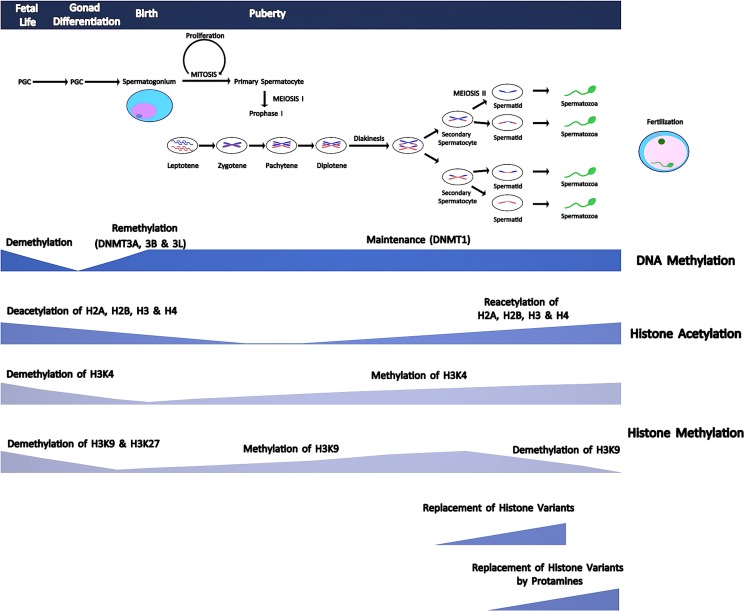
Fig. 1.
A diagram showing comparative timing of meiotic phases, DNA methylation patterns, histone tail modifications, and protamination during spermatogenesis. Meiosis starts with puberty. Methylation marks of primordial germ cells (PGCs) are erased during the embryogenesis. After this demethylation process, a specific remethylation program starts in spermatogonia and type I spermatocytes. Acetylation of H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 is high in spermatogonia, and these histones are deacetylated throughout meiosis, and round spermatids are reacetylated in elongating spermatids. Hyperacetylation of histone tails causes loosening of chromatin structure and stimulates DNA strand breaks by topoisomerase enzyme, which in turn facilitates separation of histones and replacement by transition proteins that are later replaced by protamines