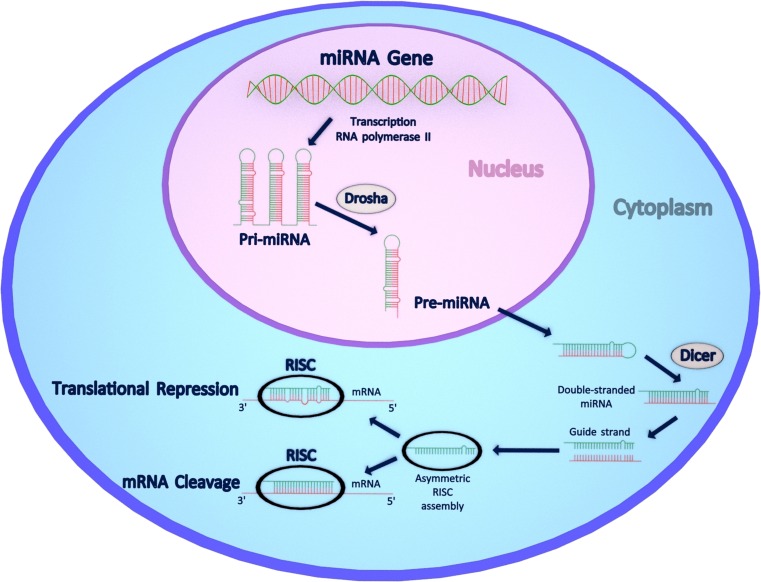
Fig. 2.
miRNA biogenesis pathway and its functional consequences for the mammalian cell. In the nucleus, miRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II to generate large precursor pri-miRNAs that are then processed by type III RNase Drosha to pre-miRNAs. Pre-miRNAs are then exported into the cytoplasm where they are further processed by the enzyme Dicer to form a mature, 21-25 nucleotide long, duplex miRNA. Of its two strands, the so-called guide strand is incorporated into the RISC complex where it base-pairs with its target mRNA sequence. Perfect base pairing results in mRNA cleavage and degradation, while imperfect pairing, mostly at 3’UTRs, causes translational repression