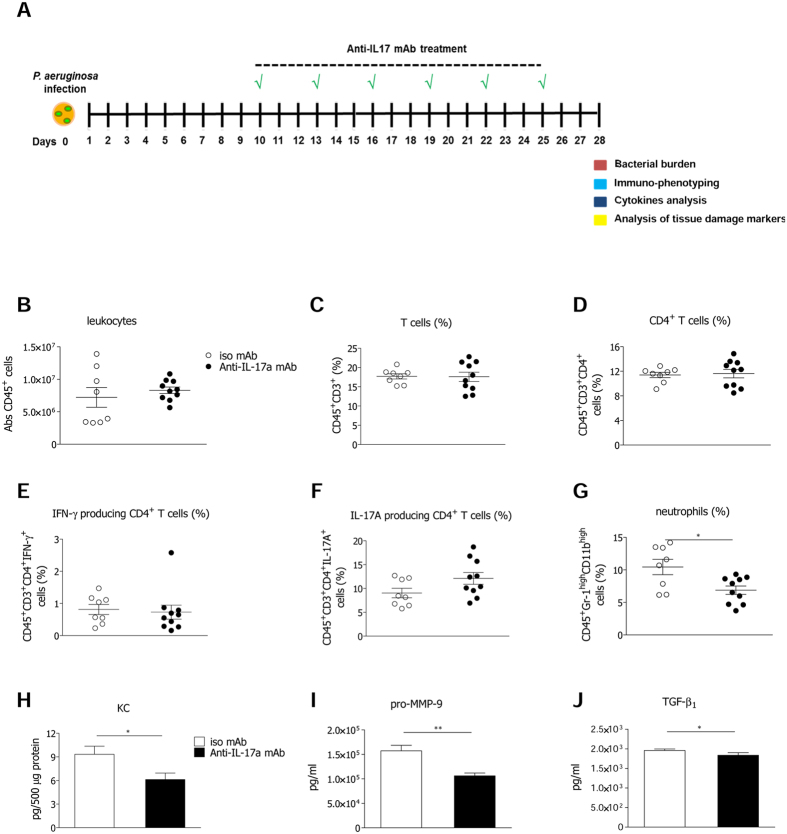
Figure 5. Anti-IL-17A mAb treatment in the murine model of chronic airways infection by P. aeruginosa.
C57Bl/6 mice were infected with 1 to 2 × 106 CFU/lung of the P. aeruginosa strain AA43 embedded in agar beads. Every three days starting from the tenth day from infection, a group of mice was treated by intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) with 100 μg/mouse of anti-IL-17A mAb, while the other group was treated with 100 μg/mouse of control isotypic IgG and analyzed after 28 days of infection. Schematic view of the treatment schedule is shown (A). Leukocytes (B), T cells (C), CD4+ T cells (D), the frequency of IFN-γ- (E) and IL-17A-producing CD4+ T cells (F) after PMA/ionomycin stimulation, and neutrophils (G) were measured by flow cytometric analysis in cell suspensions of murine lungs. Dots represent cells in individual mice, horizontal lines represent mean values and the error bars represent the SEM. KC levels (H) were measured by Bioplex in the supernatants of murine lung cellular suspensions. Levels of pro-MMP-9 (I) by ELISA and TGF-β1 (J) by Bioplex were measured in the supernatants of murine lung cellular suspensions. Values represent the mean ± SEM. The data are pooled from at least two independent experiments (n = 8–10). Statistical significance is indicated: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.