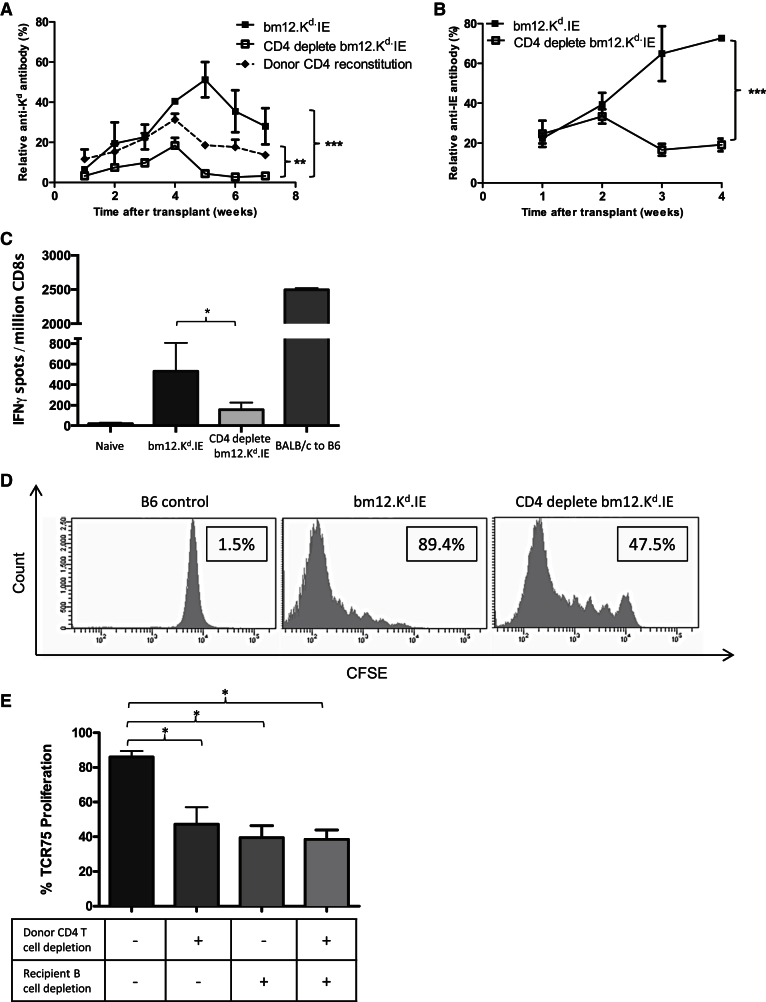
Figure 2.
GVH Recognition by Passenger Donor CD4 T Cells within the Heart Allograft Augments Conventional Host Alloimmunity
(A and B) Anti-Kd IgG alloantibody responses in B6 recipients of bm12.Kd.IE heart allografts from CD4 T cell-depleted donors (CD4 deplete bm12.Kd.IE) were significantly attenuated and restored by adoptive transfer of purified donor CD4 T cells to recipients at the time of transplant (A). Anti-I-E IgG responses were similarly abrogated (B).
(C) Cytotoxic CD8 T cell alloresponses in B6 recipients of unmodified bm12.Kd.IE heart allografts were weaker than those observed in B6 recipients of BALB/c heart grafts but significantly greater than those generated in recipients of CD4-T cell-depleted bm12.Kd.IE heart allografts.
(D and E) Indirect-pathway CD4 T cell responses, detected by quantifying proliferation of CFSE-labeled, Kd-allopeptide-specific TCR75 CD4 T cells transferred 4 weeks after transplant, expressed as a percentage of parent population divided (boxes; D), were similarly reduced in B6 recipients of CD4 T cell-depleted bm12.Kd.IE heart allografts (E). Donor CD4 T cell-mediated augmentation of host indirect-pathway CD4 T cell responses was not observed in B cell-depleted B6 recipients (E).
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA in A and B; Mann-Whitney test in C and E). Data are representative of two independent experiments (A and B; mean and SEM of n = 6 mice per group) or one experiment (C–E; mean and SEM of n = 6 mice per group in C and E or n = 6 mice per group in D).