Fig. 1.
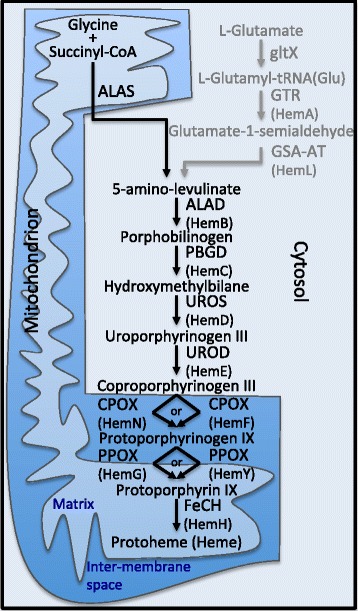
Heme pathway in eukaryotic cells. The Heme pathway in Opisthokonta, and most likely other heterotrophic eukaryotes, as described in Kořenỳ et al. [25], is represented in black. An alternate entry to the pathway, present in bacteria and in the plastids of algae, is represented in grey. For each protein name the corresponding protein in bacteria is indicated in parenthesis. The heme pathway in eukaryotes takes place in the cytosol for the steps involving ALAD, PBGD, UROS, and UROD, while ALAS and FeCH act in the mitochondrial matrix, and the PPOX and CPOX act in the inter-membrane space. Abbreviations: ALAS: 5-aminolevulinate synthase, GltX: glutamyl-tRNA synthetase, GTR: glutamyl-tRNA reductase, GSA-AT: glutamate-1-semialdehyde 2,1-aminomutase, ALAD: delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase, PBGD: porphobilinogen deaminase, UROS: uroporphyrinogen-III synthase, UROD: uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, CPOX/HemF: coproporphyrinogen III oxidase, CPOX/HemN: oxygen-independent coproporphyrinogen III oxidase, PPOX/HemY: oxygen-dependent protoporphyrinogen oxidase, PPOX/HemG: menaquinone-dependent protoporphyrinogen oxidase, FeCH: ferrochelatase
