Fig. 2.
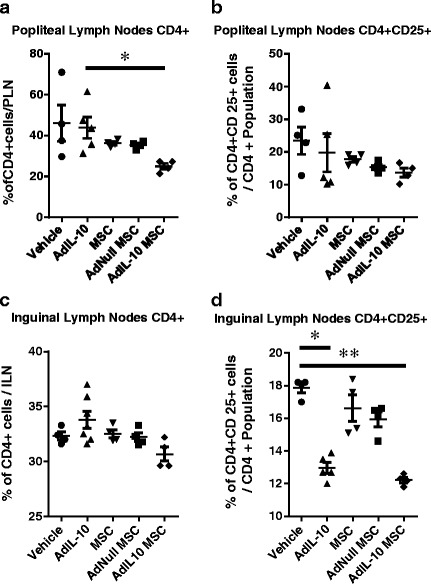
AdIL-10-transduced MSCs reduce the number of CD4+ T cells in the popliteal and inguinal lymph nodes 6 weeks after injection. CD4 and CD25 expression by lymphocytes isolated from the popliteal and inguinal lymph nodes, 6 weeks post treatment. a, b AdIL-10-transduced MSCs reduce CD4+ T-cell levels in the popliteal lymph nodes compared with AdIL-10, with no significant difference in the number of activated (CD25+) CD4 T cells between any experimental groups. c, d No significant difference was observed between any of the treatment groups in the amount of CD4+ T cells present in the inguinal lymph nodes. However, AdIL-10 only and AdIL-10-transduced MSCs significantly decreased the amount of activated CD4+ cells compared with vehicle-treated animals. Data points represent n = 4, pooled from eight animals. Data points in the AdIL-10 group represent n = 5, with three samples pooled from two animals and two single samples. Statistical significance was determined using a Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.001. Lines indicate significant difference between the individual groups. ILN inguinal lymph node, MSC mesenchymal stem cell, PLN popliteal lymph node
