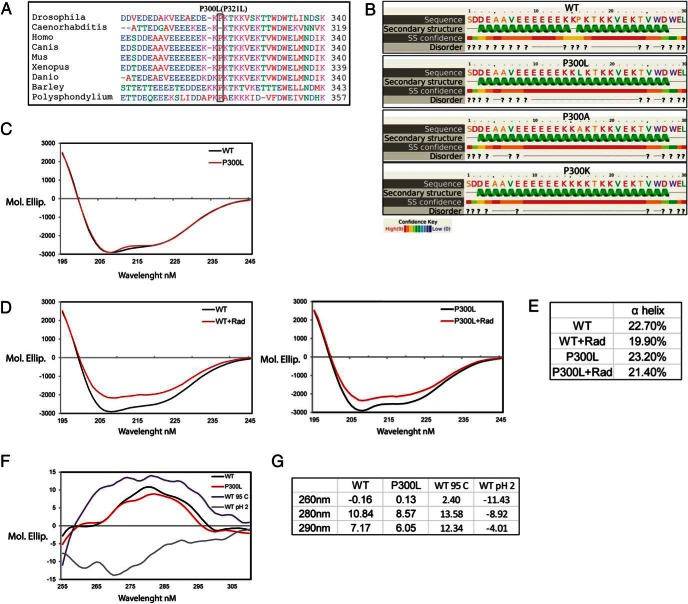
Figure 3.
P300L substitution affects tertiary but not secondary structure of GRP94 and is partially refractory to radicicol induced changes in secondary structure. A, Conservation of proline 300 of human GRP94 and other species. Amino acid sequence alignment between positions 282 and 319 of human GRP94, in the linker domain, and the corresponding sequences of indicated organisms. B, Secondary structure of amino acids 285–314 from WT, P300L, P300A, and P300K substitutions predicted using the algorithm PSIPRED (SS, secondary structure; ?, prediction of a region most likely structurally disordered). C and D, Far UV CD spectra of native N34-355 GRP94 WT and P300L variant. CD of purified GRP94 at the concentration of 1.9 μM was measured in 0.1 cm path length cuvette at 20°C. The spectra were buffer corrected. The graph represents the average of nine independent experiments. D, GRP94 WT and P300L variant were incubated for 4 hours at 4°C with 5 μM of radicicol and CD of the proteins were measured. Decrease of the spectra intensity after radicicol treatment was observed for WT GRP94 (left panel) and P300L variant (right panel). The spectra were corrected with the buffer containing radicicol. The graphs represent four independent experiments. E, Table with α-helix and turns fractions from panels D and E calculated by DichroWeb using the Selcon3 program. F, Near UV CD spectra of native N34-355 WT and P300L GRP94. Purified GRP94 was desalted into 10 mM ammonium acetate buffer to a final concentration of 7 μM. WT GRP94 was additionally incubated in 95°C or pH 2 for the period of 1 hour. CD of the proteins was measured in 1 cm path length cuvette at 20°C. The spectra were buffer corrected. The graph represents the average of four independent experiments. G, Table provides wavelength specific molecular ellipticity values for five independent experiments.