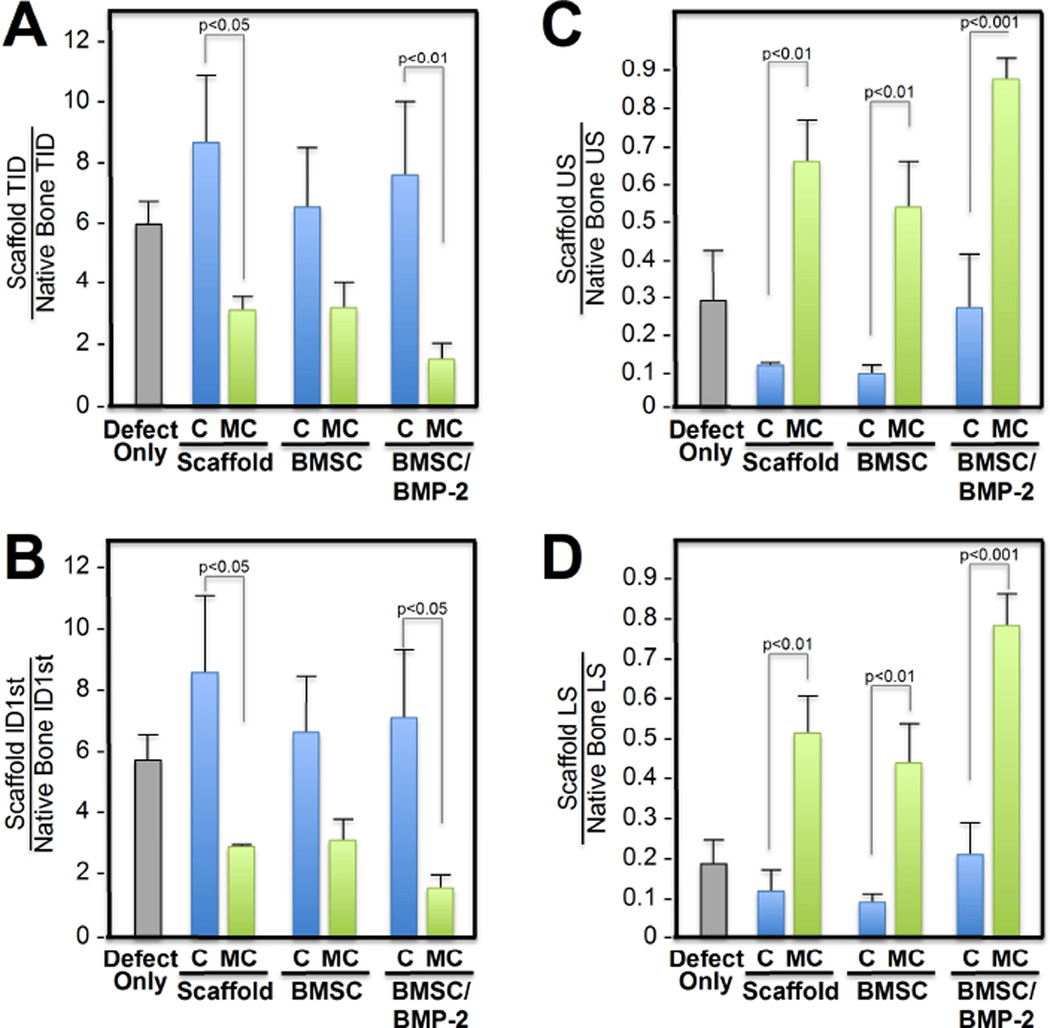
Figure 6. Biomechanical strength and stiffness of in vivo regenerated bone within Col-GAG and MC-GAG implanted cranial defects.
Reference point indentation was performed in five areas of the cranial defects implanted with scaffolds and the native calvarium to evaluate biomechanical strength and stiffness. The strength, or resistance to fracture, was measured using the total indentation distance (TID) and first cycle indentation distance (ID1st) in µm. The stiffness was measured using the loading slope (LS) and unloading slope (US). Strength and stiffness measurements were expressed as a ratio between defect and native calvarium. C, Col-GAG; MC, MC-GAG; Defect only, cranial defect without reconstruction; Scaffold, defect reconstructed with scaffolds without BMSCs or BMP-2; BMSC, defect reconstructed with scaffolds precultured with BMSCs without BMP-2; BMSC/BMP-2, defect reconstructed with scaffolds precultured with BMSCs and rhBMP-2.