Figure 4.
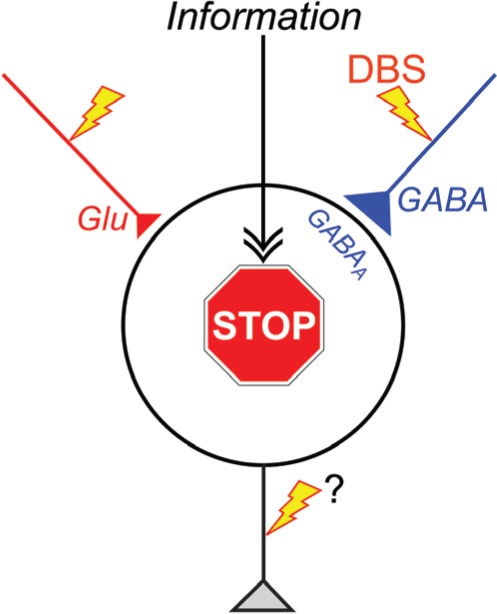
“Disruption hypothesis” explaining the mechanism underlying the effectiveness of deep brain stimulation (DBS). DBS activates axon terminals in the stimulated nucleus, induces extensive release of neurotransmitters, such as GABA and glutamate (Glu), and dissociates inputs and outputs in the stimulated nucleus. Thus, DBS results in disruption of the abnormal information flow through the cortico-basal ganglia loop in the pathological conditions. GABAA, GABAA receptors.
