Fig 5. Reduced eGFR is a late marker of podocyte depletion.
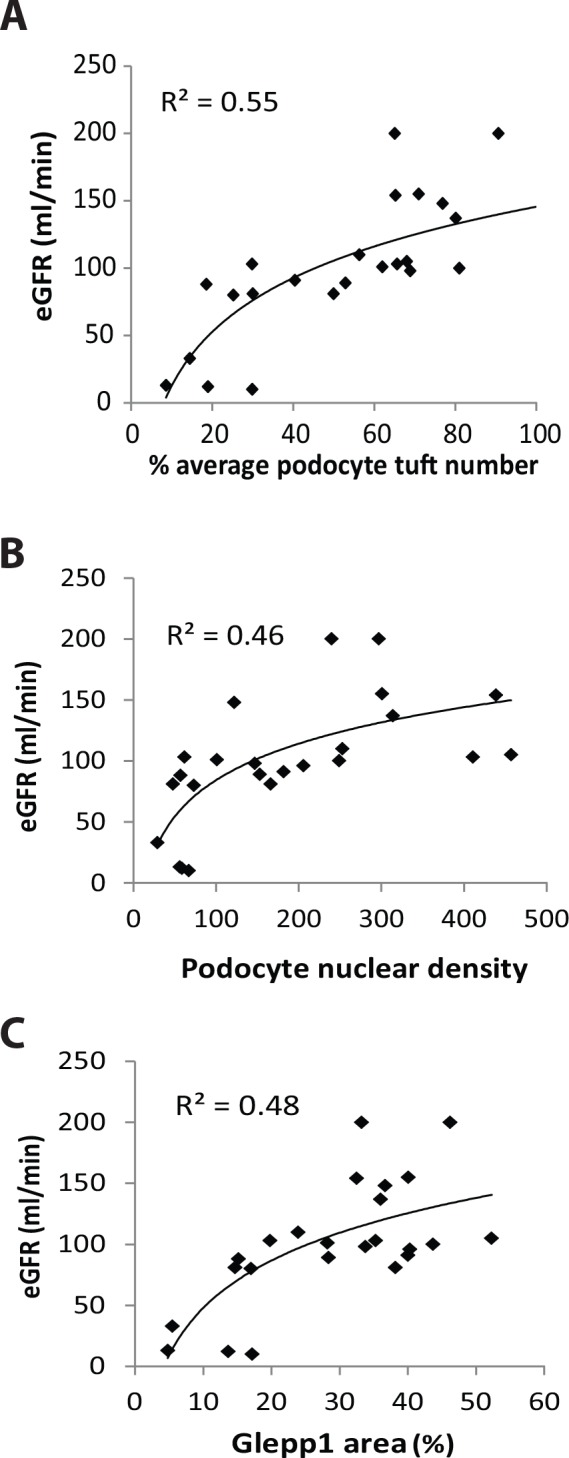
Panel A: Kidney function as measured by eGFR is detectably reduced only when podocyte depletion is reduced to the level of about 20% of normal (i.e. 80% depletion). Panel B: eGFR becomes measurably reduced when podocyte density falls below 100 per 106 um3. Panel C: eGFR becomes measurably reduced when the Glepp1% area is reduced below about 15–20%. Two eGFR values of 380 and 400 ml/min from an infant aged 2 and 3 years with a serum creatinine of 0.1mg% and high level proteinuria at the time of biopsy were excluded from analysis because of the inherent inaccuracy of the eGFR estimate under those conditions. These data collectively show that reduction in eGFR below the normal range (60ml/min) is a late marker of podocyte depletion in ASC biopsies. Logarithmic equations using best fit curve estimation are used in all panels.
