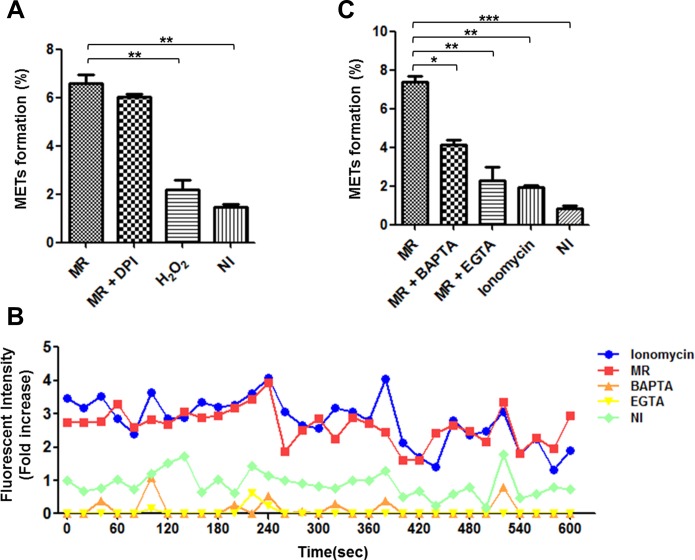
Fig 4. M. mass R-induced MET formation is not dependent on NADPH oxidase activity, but does depend on calcium influx.
After staining THP-1 macrophages with TO-PRO-3, the MET formation (%) in each sample was determined by quantification of MET-positive cells to total cell count. (A) Differentiated THP-1 macrophages were stimulated with hydrogen peroxide (1 mM), M. mass R (MOI 5) with or without DPI (20 μM) for 24 hr. (B) Fluo-4-labeled THP-1 macrophages were untreated or pretreated with BAPTA (20 μM) or EGTA (1 mM) for 30 min and then infected with M. mass R (MOI 5). Ionomycin (1 μM) was used as positive control. Intracellular calcium transients of labeled cells were recorded in a microplate reader at 6 hr after infection. (C) Determination of MET formation (%] in each sample. MR: M. mass R. Data are representative of three independent experiments. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001 compared to M. mass R-infected group by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-test.