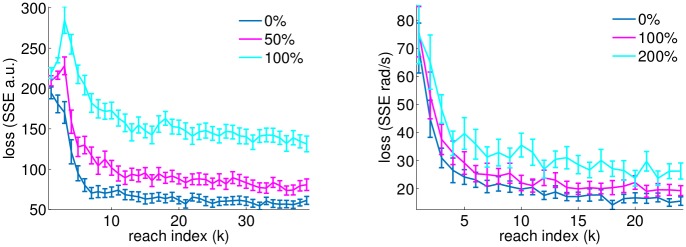
Fig 7. Plots depict decline in performance (i.e. loss between noise-free oracle and decoded intention) with intention noise model mismatch using sum square error (SSE) over the duration of a reach for (left) cursor task and (right) arm reaching task trajectories, comparable to performance curves in Figs 2 and 4 respectively.
In each task, noise performance curves are obtained when the user’s intent is a noisy version of the oracle, captured by a linear combination of intention oracle and a random vector. The noise level is indicated by a noise percentage, corresponding to the magnitude of the noise relative to the intention oracle signal. The effects of the relative noise are not directly comparable across tasks because the noise is distributed over more dimensions in the arm task.