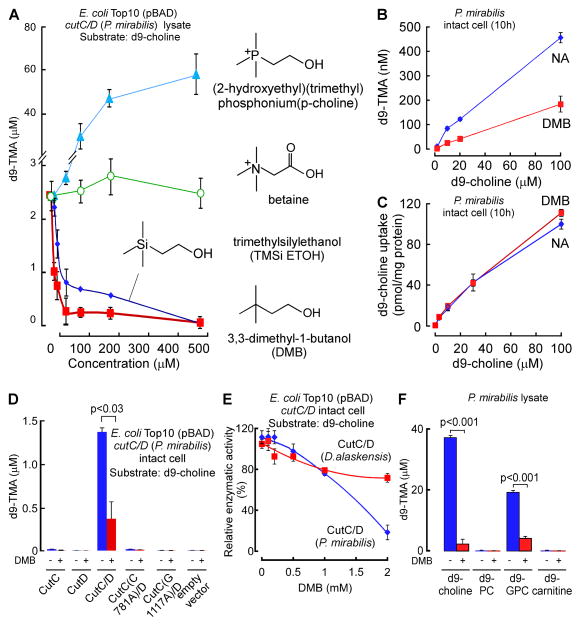
Figure 1. The choline analogue 3,3-dimethyl-1-butanol inhibits microbial choline TMA lyase activity.
(A) Effect of the indicated choline analogues on microbial TMA lyase activity (measured as d9-TMA production from 100 μM of the indicated d9-labeled substrate) from lysate of E. coli Top10 cells transformed (pBAD vector) with cutC/D genes (from P. mirabilis). (B) Effect of DMB on choline TMA lyase activity in intact P. mirabilis incubated with the indicated concentrations of d9-choline substrate ± DMB (1 mM) at 37°C. (C) DMB effect on choline uptake. P. mirabilis (OD600 nm = 0.5) were pelleted and then re-suspended in minimal media supplemented with the indicated concentrations of d9-choline ± DMB (2 mM) for 15 minutes at 37°C. Intracellular d9-choline was then quantified as described under Methods. (D) Choline TMA lyase activity from intact E. coli Top10 cells transformed with the indicated constructs in the presence vs. absence of DMB. (E) DMB dose response curves for inhibition of choline TMA lyase activity in intact E. coli Top10 cells transformed with cutC/D genes from either D. alaskensis (pUC57 vector) or P. mirabilis (pBAD vector). (F) TMA lyase activity for the indicated substrates in P. mirabilis lysate ± DMB. Data are presented as mean ± SE from three independent replicates (A–F). See also Figures S1, S2, S6.