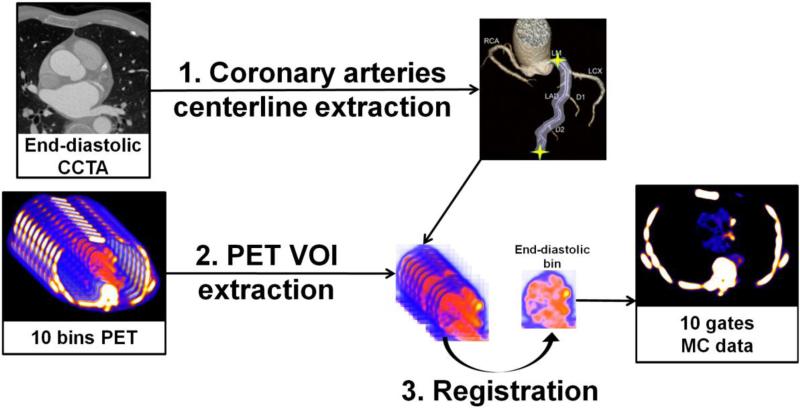
Figure 2.
Overview of the motion correction method. (1) Coronary artery centerlines are extracted from CCTA in end-diastolic phase (2) Volumes of interest (VOIs) surrounding coronary arteries are extracted from 10-bin PET data using previously extracted CCTA centerlines. (3) All bins of data are registered to common end-diastolic reference bin by nonlinear level-set or demons registration restricted to coronary regions. Then, registered VOIs are inserted back into their original PET volumes, and all registered PET images are summed into a single volume to obtain motion-corrected 10-bin data. MC = motion-corrected; VOI = volume of interest.