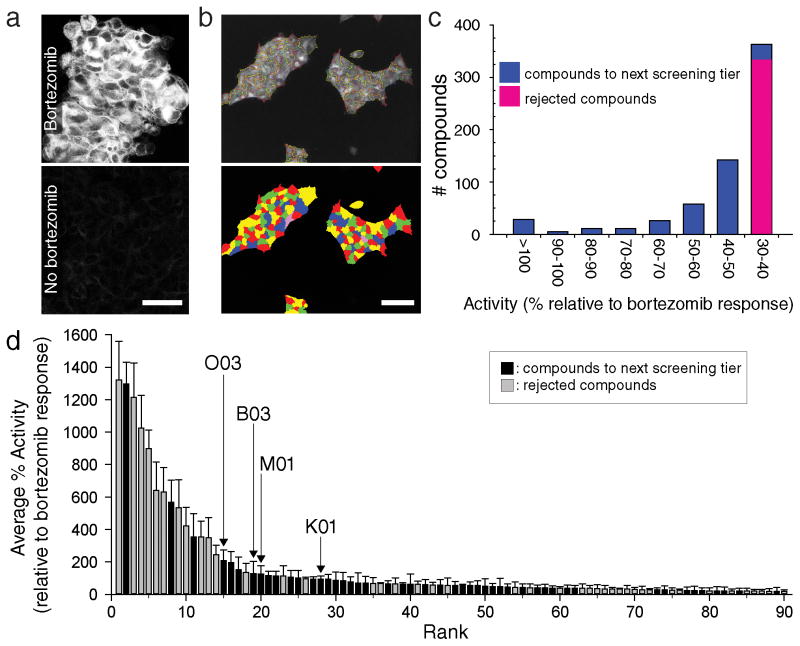
Figure 1. High-throughput screening identifies compounds that stabilize human CLRN1N48K.
(a) Inhibition of proteasomes by bortezomib increased CLRN1N48K levels in a D6 cell line stably expressing CLRN1N48K mRNA. CLRN1N48K was tagged with an HA epitope that was detected by immunofluorescence microscopy. (b) Cell-containing areas were segmented to measure relative concentrations of CLRN1N48K. Cells were outlined in the top image and colored in the bottom image. (c) Approximately 50,000 compounds were tested by high-throughput screening for stabilization of CLRN1N48K, and the measured efficacies of these compounds were normalized to 25 nM bortezomib assayed on the same plate. The top 320 compounds (blue) were selected for further analysis. (d) The top 320 compounds were subjected to the same assay 6 times. Of these, 90 compounds with highest average percentage (%) activities are shown. Among them, 48 compounds (black) were selected for secondary screening but 42 compounds (grey) were eliminated due to unfavorable properties such as autofluorescence, the formation of dye-like structures, or chemical structures unsuitable for further pharmaceutical development10,11. Data on the y-axis are presented as means ± SEMs (n = 6). Compounds O03, B03, M01, and K01 are labeled. Scale bars = 50 μm.