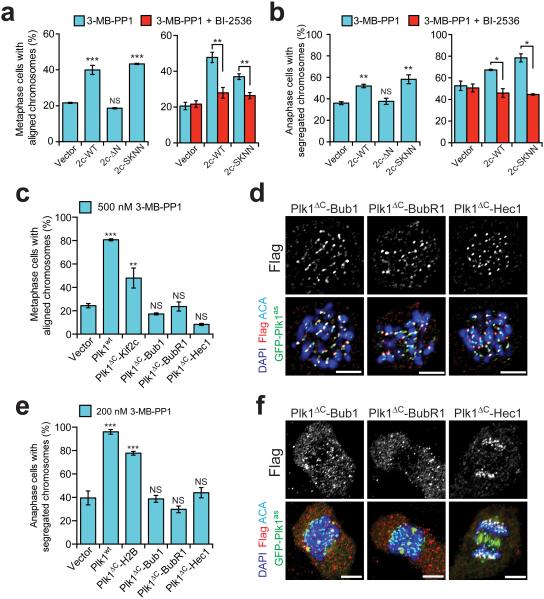
Figure 5. Outer kinetochore tethering of Plk1 fails to restore chromosome alignment or segregation.
(a-b) Cells expressing GFP-Plk1as and Kif2c localization mutants were challenged with 3-MB-PP1 ± BI-2536 and assayed for ability of constructs to rescue chromosome alignment during metaphase or segregation during anaphase. (a) Graphs show average percentage (± SEM) of pre-anaphase mitotic cells at metaphase with fully aligned chromosomes for each cell line (n=150 cells/experiment; 3 independent experiments). (b) Graph shows average percentage (± SEM) of anaphase cells with fully segregated chromosomes for each cell line (n=50 cells/experiment; 4 independent experiments). (c-f) Cells expressing GFP-Plk1as and outer kinetochore-tethered Plk1 constructs were challenged with 3-MB-PP1 and assayed for ability of constructs to rescue chromosome alignment during metaphase or segregation during anaphase. (c) As in panel a (n=150 cells/experiment; 3 independent experiments). (d) Representative single-plane micrographs indicating kinetochore localization of Plk1 tethers in cells failing to restore chromosome alignment. (e) As in panel b (n≥30 cells/experiment; 4 independent experiments). (f) Representative maximal intensity micrographs indicating localization of Plk1 tethers in cells failing to restore chromosome segregation. *P< 0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0001 by one-way ANOVA or unpaired t-test; NS, not significant (panels a,b,c,e). Scale bars, 5 μm (panel d,f).